Asked by Araceli Zambrano on Jul 30, 2024

Verified
The local community is considering two options to raise money to finance a new civic center. The first option is to institute a per unit tax on restaurant meals of $2.46. The market demand and supply functions for restaurant meals are: 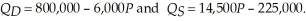 Calculate consumer and producer surplus with the per unit tax. The second option the community is considering implementing is an income tax. If an income tax is implemented, the new demand for restaurant meals is:
Calculate consumer and producer surplus with the per unit tax. The second option the community is considering implementing is an income tax. If an income tax is implemented, the new demand for restaurant meals is: 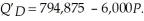 Calculate the level of consumer and producer surplus in the restaurant market with the income tax. Which of the two options will reduce the sum of consumer and producer surplus the least?
Calculate the level of consumer and producer surplus in the restaurant market with the income tax. Which of the two options will reduce the sum of consumer and producer surplus the least?
Per Unit Tax
A tax levied on goods that is fixed in amount for each unit produced or sold.
Consumer Surplus
The gap in the total funds consumers are willing and financially prepared to allocate for a good or service, versus the funds actually allocated.
Producer Surplus
The difference between the amount producers are willing to supply a good for and the actual amount they receive when the good is sold.
- Estimate the changes in consumer and producer surplus due to taxes and subsidies.
- Evaluate the efficiency and equity implications of taxation and subsidy policies.

Verified Answer
QD = 800,000 - 6,000 Pb = Qs = 14,500(Pb - 2.46) - 225,000
Pb = 51.74
The quantity exchanged will be: 489,560. The choke price (lowest price such that no units are transacted) is 133.33.
Consumer surplus is
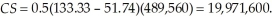 Producer surplus is
Producer surplus is 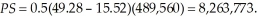 Government tax receipts are $1,204,317.60.
Government tax receipts are $1,204,317.60.Consumer and producer surplus with the tax is 28,235,373.
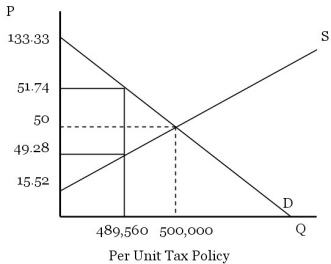 With an income tax, we need to determine the new equilibrium price and quantity.
With an income tax, we need to determine the new equilibrium price and quantity. 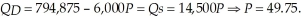 At a price of $49.75, the quantity exchanged will be: 496,375. The choke price (lowest price such that no units are transacted) is $133
At a price of $49.75, the quantity exchanged will be: 496,375. The choke price (lowest price such that no units are transacted) is $133  . The highest price such that no meals will be produced is $15.52. Consumer surplus is
. The highest price such that no meals will be produced is $15.52. Consumer surplus is 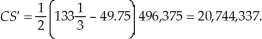 Producer surplus is
Producer surplus is 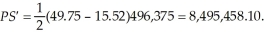 The sum of consumer and producer surplus with the income tax is $29,239,795.10. Since consumer and producer surplus is higher for the income tax, the income tax does the least harm to societal welfare than the per unit tax.
The sum of consumer and producer surplus with the income tax is $29,239,795.10. Since consumer and producer surplus is higher for the income tax, the income tax does the least harm to societal welfare than the per unit tax.
Learning Objectives
- Estimate the changes in consumer and producer surplus due to taxes and subsidies.
- Evaluate the efficiency and equity implications of taxation and subsidy policies.
Related questions
The Market Demand and Supply Functions for Easton Redline Slow-Pitch ...
The Market Demand and Supply Functions for Pizza Are ...
The Total and Marginal Cost Functions for a Typical Soft ...
The Clinton Administration Has Recommended an Increase in the Tax ...
The Market Demand and Supply Functions for Imported Cars Are ...