Asked by Sewar Rawabdeh on Jul 27, 2024

Verified
The total and marginal cost functions for a typical soft coal producer are:
TC = 75,000 + 0.1Q2 and MC = 0.2Q
where Q is measured in railroad cars per year. The industry consists of 55 identical producers. The market demand curve is:
QD = 140,000 - 425P,
where P is the price per carload. The market can be regarded as competitive.
a. Calculate the short run equilibrium price and quantity in the market. Calculate the quantity that each firm would produce. Calculate producer surplus, consumer surplus, and total surplus at the equilibrium values. Calculate the firm's profit (or loss).
b. The Federal government is considering the imposition of a $15 per carload tax on soft coal. Calculate the short-run equilibrium price and quantity that would exist under the tax. What portion of the tax would be paid by producers and what portion by consumers? Calculate the producer and consumer surplus under the tax and analyze the efficiency consequences of the tax. Calculate the firm's profit (or loss) under the tax. Could the tax be justified despite its efficiency implications?
Marginal Cost
The cost incurred to produce one additional unit of a product or service.
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity of a good demanded equals the quantity of that good supplied.
Tax Implications
The effects that taxes have on the financial outcomes of activities, including the impact on overall costs and benefits in business and personal finance.
- Gauge the effect that taxes and subsidies exert on the surplus for buyers and sellers.
- Understand the concept of deadweight loss and its causes in the context of taxation and subsidies.
- Explore the economic consequences of chosen taxes and subsidies on market equilibrium.

Verified Answer
ZK
Zybrea KnightAug 02, 2024
Final Answer :
a.To find market supply curve begin by finding firm's supply curve.Firm's supply curve is MC curve (in this case all of MC lies above AVC):
Solve for Q in terms of MC = P:
MC = 0.2Q
Q = 5P
Market short-run supply is the horizontal sum of firm supply. There are 55 firms in the market, so market supply is 55 times the individual firm's supply.
QS = 275P
Equate QD and QS to determine P and Q.
275P = 140,000 - 425P
700P = 140,000
P = $200
Q = 275(200)
Q = 55,000
Individual firm equates P to MC:
200 = 0.2Q
Q = 1,000
π = TR - TC
TR = (200)(1000)
TR = 200,000
TC = 75,000 + 0.1(1000)2
TC = 175,000
π = 25,000
Producer and consumer surplus:
Solve for P in terms of Q.
QS = 275P
P = 0.0036Q
QD = 140,000 - 425P
P = 329.41 - 0.0024Q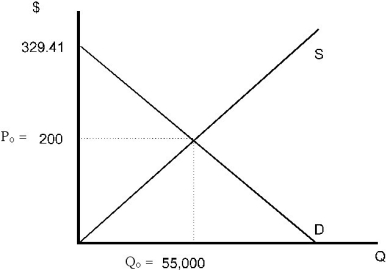 Producer surplus = 0.5(55,000)(200) = 5,500,000
Producer surplus = 0.5(55,000)(200) = 5,500,000
Consumer surplus = 0.5(55,000)(329.41 - 200) = 3,558,775
Total of producer and consumer surplus is
3,558,775 + 5,550,000 = 9,058,775
b.Pb = buyer's price
Ps = seller's price (net of tax)
Pb - Ps = 15 = tax
QD = 140,000 - 425 Pb is market demand
QS = 275 Ps is market supply
Set supply equal to demand:
140,000 - 425 Pb = 275 Ps
Pb = Ps + 15
140,000 - 425 (Ps + 15) = 275 Ps
140,000 - 425 Ps - 6,375 = 275 Ps
Ps = 190.89
Pb = Ps + 15 = 205.89
Consumers pay:
Pb - Po = 205.89 - 200 = 5.89
Producers pay:
Po - Ps = 200 - 190.89 = 9.11
Plug Ps into the supply equation to get quantity:
Q = Qs = 275 Ps = 275(190.89) = 52,495
(If you plug into the demand equation instead your answer will differ slightly due to rounding.)
Individual firm equates P to MC:
205.89 = 0.2Q + 15
Q = 954.5
π = TR - TC
TR = 205.89(954.50)
TR = 196,522
TC = 75,000 + 0.1Q2 + 15Q
TC = 180,424.53
π = 16,097.48
Profit fell from 25,000 to 16,097.48.
Producer and Consumer Surplus:
Demand curve remains: P = 329.41 - 0.0024Q
Solve for P in terms of QS.
QS = -4125 + 275P
275P = QS + 4,125
P = 15 + 0.0036 Q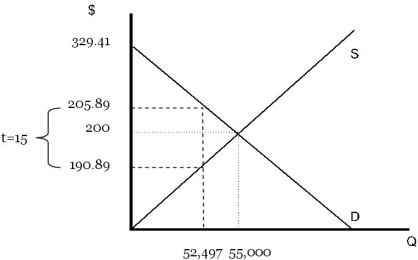 Producer surplus = 0.5(52,497)(205.89) = 5,404,303.67
Producer surplus = 0.5(52,497)(205.89) = 5,404,303.67
Consumer surplus = 0.5(52,497)(329.41 - 205.89) = 3,242,214.72
Total of Producer and Consumer Surplus:
= 5,404,303.67 + 3,242,214.72 = 8,646,518.39
Total surplus fell from 9,058,775 to 8,646,518.39.
There is a welfare loss as indicated by the loss in total surplus. The tax could be justified by known externalities of soft coal.
Solve for Q in terms of MC = P:
MC = 0.2Q
Q = 5P
Market short-run supply is the horizontal sum of firm supply. There are 55 firms in the market, so market supply is 55 times the individual firm's supply.
QS = 275P
Equate QD and QS to determine P and Q.
275P = 140,000 - 425P
700P = 140,000
P = $200
Q = 275(200)
Q = 55,000
Individual firm equates P to MC:
200 = 0.2Q
Q = 1,000
π = TR - TC
TR = (200)(1000)
TR = 200,000
TC = 75,000 + 0.1(1000)2
TC = 175,000
π = 25,000
Producer and consumer surplus:
Solve for P in terms of Q.
QS = 275P
P = 0.0036Q
QD = 140,000 - 425P
P = 329.41 - 0.0024Q
 Producer surplus = 0.5(55,000)(200) = 5,500,000
Producer surplus = 0.5(55,000)(200) = 5,500,000Consumer surplus = 0.5(55,000)(329.41 - 200) = 3,558,775
Total of producer and consumer surplus is
3,558,775 + 5,550,000 = 9,058,775
b.Pb = buyer's price
Ps = seller's price (net of tax)
Pb - Ps = 15 = tax
QD = 140,000 - 425 Pb is market demand
QS = 275 Ps is market supply
Set supply equal to demand:
140,000 - 425 Pb = 275 Ps
Pb = Ps + 15
140,000 - 425 (Ps + 15) = 275 Ps
140,000 - 425 Ps - 6,375 = 275 Ps
Ps = 190.89
Pb = Ps + 15 = 205.89
Consumers pay:
Pb - Po = 205.89 - 200 = 5.89
Producers pay:
Po - Ps = 200 - 190.89 = 9.11
Plug Ps into the supply equation to get quantity:
Q = Qs = 275 Ps = 275(190.89) = 52,495
(If you plug into the demand equation instead your answer will differ slightly due to rounding.)
Individual firm equates P to MC:
205.89 = 0.2Q + 15
Q = 954.5
π = TR - TC
TR = 205.89(954.50)
TR = 196,522
TC = 75,000 + 0.1Q2 + 15Q
TC = 180,424.53
π = 16,097.48
Profit fell from 25,000 to 16,097.48.
Producer and Consumer Surplus:
Demand curve remains: P = 329.41 - 0.0024Q
Solve for P in terms of QS.
QS = -4125 + 275P
275P = QS + 4,125
P = 15 + 0.0036 Q
 Producer surplus = 0.5(52,497)(205.89) = 5,404,303.67
Producer surplus = 0.5(52,497)(205.89) = 5,404,303.67Consumer surplus = 0.5(52,497)(329.41 - 205.89) = 3,242,214.72
Total of Producer and Consumer Surplus:
= 5,404,303.67 + 3,242,214.72 = 8,646,518.39
Total surplus fell from 9,058,775 to 8,646,518.39.
There is a welfare loss as indicated by the loss in total surplus. The tax could be justified by known externalities of soft coal.

Learning Objectives
- Gauge the effect that taxes and subsidies exert on the surplus for buyers and sellers.
- Understand the concept of deadweight loss and its causes in the context of taxation and subsidies.
- Explore the economic consequences of chosen taxes and subsidies on market equilibrium.
Related questions
The Deadweight Loss of a Specific Tax Will Be a ...
The Local Community Is Considering Two Options to Raise Money ...
What Is the Welfare Impact of a Subsidy Policy ...
Why Is There a Deadweight Loss Associated with Subsidy Payments ...
The Clinton Administration Has Recommended an Increase in the Tax ...