Asked by Neupane Saroj on May 29, 2024

Verified
Carcana Corporation has two manufacturing departments--Machining and Finishing.The company used the following data at the beginning of the period to calculate predetermined overhead rates: 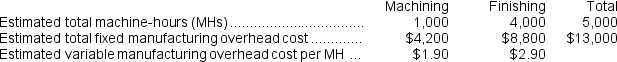 During the period, the company started and completed two jobs--Job E and Job G.Data concerning those two jobs follow:
During the period, the company started and completed two jobs--Job E and Job G.Data concerning those two jobs follow:  Required:
Required:
a.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both departments.What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Machining department?
b.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments.What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Finishing department?
c.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments.How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job E?
d.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments.How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job G?
e.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments.Further assume that the company uses a markup of 80% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices.Calculate the selling price for Job E.
f.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments.Further assume that the company uses a markup of 80% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices.Calculate the selling price for Job G.
g.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments.If both jobs were sold during the month, what was the company's cost of goods sold for the month?
Departmental Overhead Rates
Specific overhead rates calculated for different departments within a company, reflecting the unique costs each department incurs.
Machine-Hours
A measure of production output or activity based on the number of hours machines are operating.
Manufacturing Overhead
All manufacturing costs that are not direct materials or direct labor, including indirect expenses like maintenance and utilities.
- Calculate and apply departmental predetermined overhead rates.
- Understand the difference between plantwide and departmental predetermined overhead rates.
- employ manufacturing expense data to set selling prices with the use of markup percentages.

Verified Answer
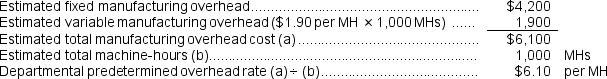 b.Finishing Department predetermined overhead rate:
b.Finishing Department predetermined overhead rate: 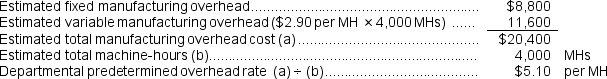 c.Manufacturing overhead applied to Job E:
c.Manufacturing overhead applied to Job E:  d.Manufacturing overhead applied to Job G:
d.Manufacturing overhead applied to Job G:  e.The selling price for Job E would be calculated as follows:
e.The selling price for Job E would be calculated as follows: 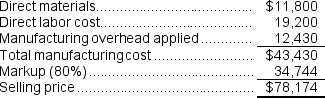 f.The selling price for Job G would be calculated as follows:
f.The selling price for Job G would be calculated as follows: 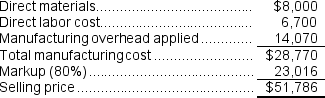 g.
g. 

Learning Objectives
- Calculate and apply departmental predetermined overhead rates.
- Understand the difference between plantwide and departmental predetermined overhead rates.
- employ manufacturing expense data to set selling prices with the use of markup percentages.
Related questions
Dancel Corporation Has Two Production Departments, Milling and Finishing ...
Assume That the Company Uses Departmental Predetermined Overhead Rates with ...
Morataya Corporation Has Two Manufacturing Departments--Machining and Assembly ...
Tarrant Corporation Has Two Manufacturing Departments--Casting and Finishing ...
Lupo Corporation Uses a Job-Order Costing System with a Single ...