Asked by devanshi mehrotra on May 09, 2024

Verified
Lupo Corporation uses a job-order costing system with a single plantwide predetermined overhead rate based on machine-hours. The company based its predetermined overhead rate for the current year on the following data: 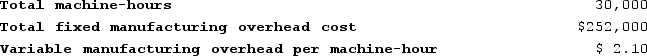 Recently, Job T687 was completed with the following characteristics:
Recently, Job T687 was completed with the following characteristics:
 If the company marks up its unit product costs by 40% then the selling price for a unit in Job T687 is closest to: (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
If the company marks up its unit product costs by 40% then the selling price for a unit in Job T687 is closest to: (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
A) $81.60
B) $305.60
C) $285.60
D) $241.50
Predetermined Overhead Rate
An estimated charge per unit of activity used to allocate manufacturing overhead costs to products or job orders, calculated before the period begins based on expected costs and activity levels.
Machine-Hours
A measure of the amount of time a machine is operated in the production process, used as a basis for allocating manufacturing overhead.
Markup
The sum added onto the purchase price of merchandise to cover both overhead expenses and profit, ultimately setting the retail price.
- Compute and comprehend sales pricing by considering production expenses and profit margin percentages.

Verified Answer
Direct materials cost = $1,200 + $1,800 = $3,000
Direct labor cost = 150 hours x $16 per hour = $2,400
Manufacturing overhead cost = 150 machine-hours x $40 per machine-hour = $6,000
Total manufacturing cost = $3,000 + $2,400 + $6,000 = $11,400
Next, we need to add the markup of 40% to the total manufacturing cost:
Total cost with markup = $11,400 x 1.4 = $15,960
Finally, we can calculate the selling price for one unit in Job T687, which used a total of 300 machine-hours:
Selling price per unit = $15,960 / 300 units = $53.20 per unit
Therefore, the selling price for a unit in Job T687 is closest to $285.60 (which is $53.20 x 5 units in the job). The correct choice is C.

Learning Objectives
- Compute and comprehend sales pricing by considering production expenses and profit margin percentages.
Related questions
Opunui Corporation Has Two Manufacturing Departments--Molding and Finishing ...
Nielsen Corporation Has Two Manufacturing Departments--Machining and Assembly ...
Carcana Corporation Has Two Manufacturing Departments--Machining and Finishing ...
Dancel Corporation Has Two Production Departments, Milling and Finishing ...
Cull Corporation Uses a Job-Order Costing System with a Single ...