Asked by Cristina Valadez on Jun 20, 2024

Verified
Which of the following statements concerning the unit product cost of Product I4 is true?
A) The unit product cost of Product I4 under traditional costing is greater than its unit product under activity-based costing by $20.40.
B) The unit product cost of Product I4 under traditional costing is greater than its unit product under activity-based costing by $257.16.
C) The unit product cost of Product I4 under traditional costing is less than its unit product cost under activity-based costing by $257.16.
D) The unit product cost of Product I4 under traditional costing is less than its unit product cost under activity-based costing by $20.40.
Unit Product Cost
The total expense incurred to produce, store, and sell one unit of a product.
Traditional Costing
A costing method that allocates overhead based on a single predetermined rate.
Activity-Based Costing
A costing methodology that assigns overhead and indirect costs to specific activities, improving accuracy in product costing by identifying cost drivers.
- Understand the fundamentals of activity-based costing and distinguish between traditional costing methods and ABC.
- Evaluate the effects of costing techniques on the calculation of product costs.

Verified Answer
DR
Doris RiveraJun 25, 2024
Final Answer :
A
Explanation :
Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total overhead ÷ Total direct labor-hours
= $368,750 ÷ 4,200 DLHs = $87.80 per DLH (rounded)
Computation of traditional unit product cost: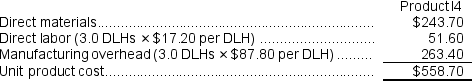 Computation of activity rates:
Computation of activity rates: 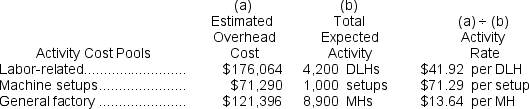 Computation of the overhead cost per unit under activity-based costing.
Computation of the overhead cost per unit under activity-based costing.  Computation of unit product cost under activity-based costing.
Computation of unit product cost under activity-based costing. 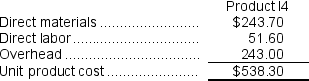 The difference in unit product costs is:
The difference in unit product costs is: 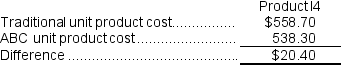 The unit product cost of Product I4 under traditional costing is greater than its unit product under activity-based costing by $20.40.
The unit product cost of Product I4 under traditional costing is greater than its unit product under activity-based costing by $20.40.
Reference: CH04-Ref29
Appleby, Inc., manufactures and sells two products: Product Q9 and Product V8.Data concerning the expected production of each product and the expected total direct labor-hours (DLHs)required to produce that output appear below: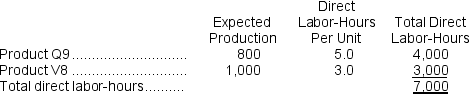 The direct labor rate is $29.30 per DLH.The direct materials cost per unit is $174.80 for Product Q9 and $168.90 for Product V8.
The direct labor rate is $29.30 per DLH.The direct materials cost per unit is $174.80 for Product Q9 and $168.90 for Product V8.
The company is considering adopting an activity-based costing system with the following activity cost pools, activity measures, and expected activity: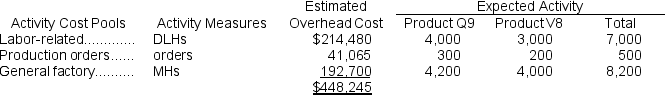
= $368,750 ÷ 4,200 DLHs = $87.80 per DLH (rounded)
Computation of traditional unit product cost:
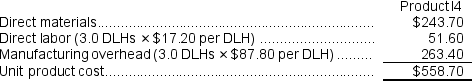 Computation of activity rates:
Computation of activity rates: 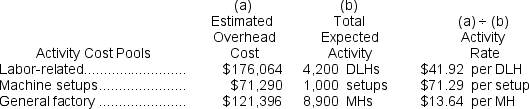 Computation of the overhead cost per unit under activity-based costing.
Computation of the overhead cost per unit under activity-based costing.  Computation of unit product cost under activity-based costing.
Computation of unit product cost under activity-based costing. 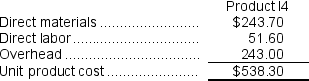 The difference in unit product costs is:
The difference in unit product costs is: 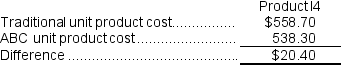 The unit product cost of Product I4 under traditional costing is greater than its unit product under activity-based costing by $20.40.
The unit product cost of Product I4 under traditional costing is greater than its unit product under activity-based costing by $20.40.Reference: CH04-Ref29
Appleby, Inc., manufactures and sells two products: Product Q9 and Product V8.Data concerning the expected production of each product and the expected total direct labor-hours (DLHs)required to produce that output appear below:
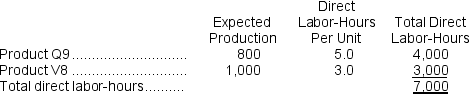 The direct labor rate is $29.30 per DLH.The direct materials cost per unit is $174.80 for Product Q9 and $168.90 for Product V8.
The direct labor rate is $29.30 per DLH.The direct materials cost per unit is $174.80 for Product Q9 and $168.90 for Product V8.The company is considering adopting an activity-based costing system with the following activity cost pools, activity measures, and expected activity:


Learning Objectives
- Understand the fundamentals of activity-based costing and distinguish between traditional costing methods and ABC.
- Evaluate the effects of costing techniques on the calculation of product costs.
Related questions
Which of the Following Statements Concerning the Unit Product Cost ...
Faiella, Inc ...
Adelberg Corporation Makes Two Products: Product a and Product B ...
Figge and Mathews Public Limited Company, a Consulting Firm, Uses ...
Desjarlais Corporation Uses the Following Activity Rates from Its Activity-Based ...