Asked by Teigan Catlin on May 29, 2024

Verified
Stockmaster Corporation has two manufacturing departments--Forming and Assembly.The company used the following data at the beginning of the year to calculate predetermined overhead rates: 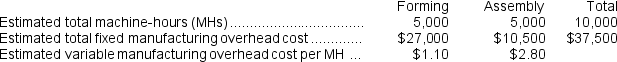 During the most recent month, the company started and completed two jobs--Job C and Job H.There were no beginning inventories.Data concerning those two jobs follow:
During the most recent month, the company started and completed two jobs--Job C and Job H.There were no beginning inventories.Data concerning those two jobs follow:  Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours and uses a markup of 40% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices.The calculated selling price for Job C is closest to:
Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours and uses a markup of 40% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices.The calculated selling price for Job C is closest to:
A) $96,989
B) $88,172
C) $25,192
D) $62,980
Predetermined Overhead Rate
A rate calculated before a period begins, used to apply overhead costs to products based on a certain activity such as labor hours or machine hours.
Machine-Hours
A measure of the amount of time machines are operating in the production process, often used to allocate manufacturing overhead costs.
Markup
The amount added to the cost price of goods to cover overhead and profit, calculated as a percentage of the cost.
- Calculate the distribution of manufacturing overhead costs to distinct work tasks and acknowledge its effect on the costing processes of jobs.
- Determine and evaluate the sale price of tasks through the application of cost-plus pricing methods and the use of manufacturing overhead rates.

Verified Answer
Job C:
Total manufacturing cost = Direct materials + Direct labor + Manufacturing overhead = $18,450 + $13,400 + ($22 x 990) = $41,340
Markup on manufacturing cost = 40%
Selling price = Manufacturing cost x (1 + Markup) = $41,340 x 1.4 = $57,876
Job H:
Total manufacturing cost = Direct materials + Direct labor + Manufacturing overhead = $21,500 + $12,100 + ($22 x 1,980) = $63,260
Markup on manufacturing cost = 40%
Selling price = Manufacturing cost x (1 + Markup) = $63,260 x 1.4 = $88,172
Therefore, the calculated selling price for Job C is closest to $57,876, which is option B.
Forming
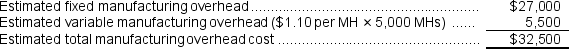 Assembly
Assembly 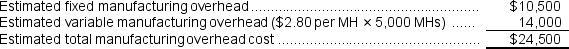 The second step is to combine the estimated manufacturing overhead costs in the two departments ($32,500 + $24,500 = $57,000)to calculate the plantwide predetermined overhead rate as follow:
The second step is to combine the estimated manufacturing overhead costs in the two departments ($32,500 + $24,500 = $57,000)to calculate the plantwide predetermined overhead rate as follow: 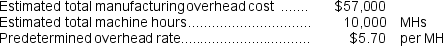 The overhead applied to Job C is calculated as follows:
The overhead applied to Job C is calculated as follows:Overhead applied to a particular job = Predetermined overhead rate x Machine-hours incurred by the job
= $5.70 per MH x (3,400 MHs + 2,000 MHs)
= $5.70 per MH x (5,400 MHs)
= $30,780
Job C's manufacturing cost:
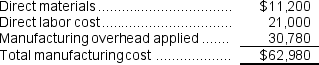 The selling price for Job C:
The selling price for Job C: 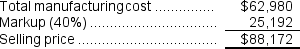

Learning Objectives
- Calculate the distribution of manufacturing overhead costs to distinct work tasks and acknowledge its effect on the costing processes of jobs.
- Determine and evaluate the sale price of tasks through the application of cost-plus pricing methods and the use of manufacturing overhead rates.
Related questions
Doakes Corporation Uses a Job-Order Costing System with a Single ...
Juanita Corporation Uses a Job-Order Costing System and Applies Overhead ...
Parido Corporation Has Two Manufacturing Departments--Casting and Assembly ...
Coates Corporation Uses a Job-Order Costing System with a Single ...
Leisure Life Manufactures a Variety of Sporting Equipment ...