Asked by Vaishnavi Surnis on May 19, 2024

Verified
EMD Corporation manufactures two products, Product S and Product W. Product W is of fairly recent origin, having been developed as an attempt to enter a market closely related to that of Product W. Product W is the more complex of the two products, requiring 3 hours of direct labor time per unit to manufacture compared to 1 hour of direct labor time for Product S. Product W is produced on an automated production line.Overhead is currently assigned to the products on the basis of direct-labor-hours. The company estimated it would incur $998,780 in manufacturing overhead costs and produce 15,000 units of Product W and 75,000 units of Product S during the current year. Unit cost for materials and direct labor are:
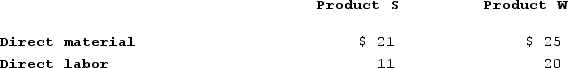 Required: a. Compute the predetermined overhead rate under the current method of allocation and determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year. b. The company's overhead costs can be attributed to four major activities. These activities and the amount of overhead cost attributable to each for the current year are given below:
Required: a. Compute the predetermined overhead rate under the current method of allocation and determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year. b. The company's overhead costs can be attributed to four major activities. These activities and the amount of overhead cost attributable to each for the current year are given below:
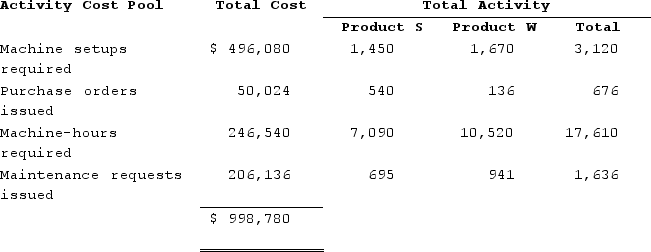 Using the data above and an activity-based costing approach, determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.
Using the data above and an activity-based costing approach, determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.
Direct Labor Time
The amount of time that workers directly involved in the production process spend on the manufacture of products, critical for costing and efficiency analysis.
Automated Production Line
A sequence of automated machines and workstations arranged to efficiently manufacture a product.
- Compute the overhead rates and utilize them for the costing of products.
- Calculate product margins by employing activity-based costing techniques.

Verified Answer
![a.The company expects to work {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours during the current year, computed as follows: Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = ${{[a(3)]:#,###}} ÷ {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours = ${{[a(30)]:#,###.00}} per direct labor-hourUsing this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be: b.The overhead rates are computed as follows: The overhead cost charged to each product is: The overhead cost charged to Product S is: Overhead cost per unit of Product S = ${{[a(63)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(5)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(77)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)The overhead cost charged to Product W is: Overhead cost per unit of Product W = ${{[a(76)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(4)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(78)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be:](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8314/11eb6b8f_61a8_31b8_bf83_d9febfd6401c_TB8314_00.jpg) Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = ${{[a(3)]:#,###}} ÷ {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours = ${{[a(30)]:#,###.00}} per direct labor-hourUsing this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be:
Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = ${{[a(3)]:#,###}} ÷ {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours = ${{[a(30)]:#,###.00}} per direct labor-hourUsing this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be:![a.The company expects to work {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours during the current year, computed as follows: Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = ${{[a(3)]:#,###}} ÷ {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours = ${{[a(30)]:#,###.00}} per direct labor-hourUsing this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be: b.The overhead rates are computed as follows: The overhead cost charged to each product is: The overhead cost charged to Product S is: Overhead cost per unit of Product S = ${{[a(63)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(5)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(77)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)The overhead cost charged to Product W is: Overhead cost per unit of Product W = ${{[a(76)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(4)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(78)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be:](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8314/11eb6b8f_61a8_31b9_bf83_ffeda2f788ce_TB8314_00.jpg) b.The overhead rates are computed as follows:
b.The overhead rates are computed as follows:![a.The company expects to work {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours during the current year, computed as follows: Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = ${{[a(3)]:#,###}} ÷ {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours = ${{[a(30)]:#,###.00}} per direct labor-hourUsing this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be: b.The overhead rates are computed as follows: The overhead cost charged to each product is: The overhead cost charged to Product S is: Overhead cost per unit of Product S = ${{[a(63)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(5)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(77)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)The overhead cost charged to Product W is: Overhead cost per unit of Product W = ${{[a(76)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(4)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(78)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be:](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8314/11eb6b8f_61a8_31ba_bf83_b9c060d619dd_TB8314_00.jpg) The overhead cost charged to each product is:
The overhead cost charged to each product is:The overhead cost charged to Product S is:
![a.The company expects to work {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours during the current year, computed as follows: Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = ${{[a(3)]:#,###}} ÷ {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours = ${{[a(30)]:#,###.00}} per direct labor-hourUsing this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be: b.The overhead rates are computed as follows: The overhead cost charged to each product is: The overhead cost charged to Product S is: Overhead cost per unit of Product S = ${{[a(63)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(5)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(77)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)The overhead cost charged to Product W is: Overhead cost per unit of Product W = ${{[a(76)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(4)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(78)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be:](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8314/11eb6b8f_61a8_31bb_bf83_190321acc014_TB8314_00.jpg) Overhead cost per unit of Product S = ${{[a(63)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(5)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(77)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)The overhead cost charged to Product W is:
Overhead cost per unit of Product S = ${{[a(63)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(5)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(77)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)The overhead cost charged to Product W is:![a.The company expects to work {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours during the current year, computed as follows: Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = ${{[a(3)]:#,###}} ÷ {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours = ${{[a(30)]:#,###.00}} per direct labor-hourUsing this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be: b.The overhead rates are computed as follows: The overhead cost charged to each product is: The overhead cost charged to Product S is: Overhead cost per unit of Product S = ${{[a(63)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(5)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(77)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)The overhead cost charged to Product W is: Overhead cost per unit of Product W = ${{[a(76)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(4)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(78)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be:](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8314/11eb6b8f_61a8_58cc_bf83_3ddbcbddb06c_TB8314_00.jpg) Overhead cost per unit of Product W = ${{[a(76)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(4)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(78)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be:
Overhead cost per unit of Product W = ${{[a(76)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(4)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(78)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be:![a.The company expects to work {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours during the current year, computed as follows: Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = ${{[a(3)]:#,###}} ÷ {{[a(29)]:#,###}} direct labor-hours = ${{[a(30)]:#,###.00}} per direct labor-hourUsing this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be: b.The overhead rates are computed as follows: The overhead cost charged to each product is: The overhead cost charged to Product S is: Overhead cost per unit of Product S = ${{[a(63)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(5)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(77)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)The overhead cost charged to Product W is: Overhead cost per unit of Product W = ${{[a(76)]:#,###.00}} ÷ {{[a(4)]:#,###}} units = ${{[a(78)]:#,###.00}} per unit (rounded)Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be:](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8314/11eb6b8f_61a8_58cd_bf83_a1c299e7fb97_TB8314_00.jpg)

Learning Objectives
- Compute the overhead rates and utilize them for the costing of products.
- Calculate product margins by employing activity-based costing techniques.
Related questions
Howell Corporation's Activity-Based Costing System Has Three Activity Cost Pools--Machining ...
Data Concerning Three of Kilmon Corporation's Activity Cost Pools Appear ...
Musich Corporation Has an Activity-Based Costing System with Three Activity ...
Groleau Corporation Has an Activity-Based Costing System with Three Activity ...
Activity Rates from Mcelderry Corporation's Activity-Based Costing System Are Listed ...