Asked by Katherine Lupercio on May 18, 2024

Verified
Doby Corporation makes a product with the following standard costs:
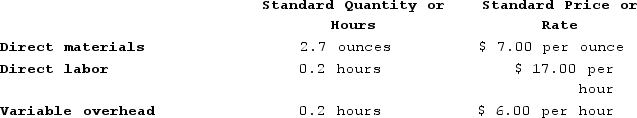 In July the company produced 4,800 units using 13,450 ounces of the direct material and 970 direct labor-hours. During the month the company purchased 14,600 ounces of the direct material at a price of $7.20 per ounce. The actual direct labor rate was $16.20 per hour and the actual variable overhead rate was $5.40 per hour. The materials price variance is computed when materials are purchased. Variable overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor-hours.
In July the company produced 4,800 units using 13,450 ounces of the direct material and 970 direct labor-hours. During the month the company purchased 14,600 ounces of the direct material at a price of $7.20 per ounce. The actual direct labor rate was $16.20 per hour and the actual variable overhead rate was $5.40 per hour. The materials price variance is computed when materials are purchased. Variable overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor-hours.
Required:
a. Compute the materials quantity variance.
b. Compute the materials price variance.
c. Compute the labor efficiency variance.
d. Compute the labor rate variance.
e. Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance.
f. Compute the variable overhead rate variance.
Materials Price Variance
The difference between the actual cost of materials used in production and the standard cost that was expected or budgeted.
Labor Efficiency Variance
The difference between the actual hours worked and the standard hours expected to produce a certain amount of goods, multiplied by the standard labor rate, indicating efficiency in labor use.
Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance
The difference between the actual variable overhead incurred and the standard cost allocated, based on the actual production volume.
- Quantify the difference in actual versus planned costs for direct materials and direct labor.
- Review and make sense of the price and quantity variances in materials.
- Measure and decode the variations found in direct labor rate and its efficiency.

Verified Answer
Materials quantity variance = (Actual quantity − Standard quantity) × Standard price
= (13,450 ounces − 12,960 ounces) × $7.00 per ounce
= (490 ounces) × $7.00 per ounce
= $3,430 Unfavorable
b. Materials price variance = Actual quantity × (Actual price − Standard price)
= 14,600 ounces × ($7.20 per ounce − $7.00 per ounce)
= 14,600 ounces × ($0.20 per ounce))
= $2,920 Unfavorable
c. Standard hours = 4,800 units × 0.2 hours per unit = 960 hours
Labor efficiency variance = (Actual hours − Standard hours) × Standard rate
= (970 hours − 960 hours) × $17.00 per hour)
= (10 hours) × $17.00 per hour)
= $170 Unfavorable
d. Labor rate variance = Actual hours × (Actual rate − Standard rate)
= 970 hours × ($16.20 per hour − $17.00 per hour)
= 970 hours × (−$0.80 per hour)
= $776 Favorable
e. Standard hours = 4,800 units × 0.2 hours per unit = 960 hours
Variable overhead efficiency variance = (Actual hours − Standard hours) × Standard rate
= (970 hours − 960 hours) × $6.00 per hour
= (10 hours) × $6.00 per hour
= $60 Unfavorable
f. Variable overhead rate variance = Actual hours × (Actual rate − Standard rate)
= 970 hours × ($5.40 per hour − $6.00 per hour)
= 970 hours × (−$0.60 per hour)
= $582 Favorable

Learning Objectives
- Quantify the difference in actual versus planned costs for direct materials and direct labor.
- Review and make sense of the price and quantity variances in materials.
- Measure and decode the variations found in direct labor rate and its efficiency.
Related questions
Camps Incorporated Has a Standard Cost System ...
Heye Incorporated Has Provided the Following Data Concerning One of ...
Sakelaris Corporation Makes a Product with the Following Standard Costs ...
Becka Incorporated Has Provided the Following Data Concerning One of ...
The Standards for Product V28 Call for 8 ...