Asked by Hannah Silene on Jun 14, 2024

Verified
Sakelaris Corporation makes a product with the following standard costs:
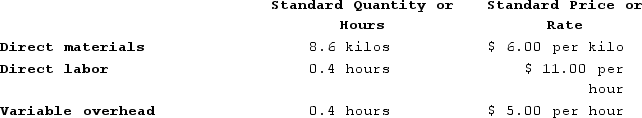 The company reported the following results concerning this product in August.
The company reported the following results concerning this product in August.
 The company applies variable overhead on the basis of direct labor-hours. The direct materials purchases variance is computed when the materials are purchased.
The company applies variable overhead on the basis of direct labor-hours. The direct materials purchases variance is computed when the materials are purchased.
Required:
a. Compute the materials quantity variance.
b. Compute the materials price variance.
c. Compute the labor efficiency variance.
d. Compute the labor rate variance.
e. Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance.
f. Compute the variable overhead rate variance.
Materials Price Variance
The difference between the actual cost of materials and the expected (or standard) cost, used to control and manage costs.
Labor Efficiency Variance
The difference between the actual hours worked and the standard hours expected to complete a task, multiplied by the standard hourly labor rate.
- Calculate variances between actual and standard costs for direct materials and direct labor.
- Investigate and interpret the differential in materials' pricing and volume.
- Execute computation and detailed explanation of direct labor rate and efficiency discrepancies.

Verified Answer
SZ
Steve Zangwa
Jun 18, 2024
Final Answer :
a. Standard quantity = 8,400 units × 8.6 kilos per unit = 72,240 kilos
Materials quantity variance = (Actual quantity − Standard quantity) × Standard price
= (71,750 kilos − 72,240 kilos) × $6.00 per kilo
= (−490 kilos) × $6.00 per kilo
= $2,940 Favorable
b. Materials price variance = (Actual quantity × Actual price) − (Actual quantity × Standard price)
= ($469,090) − (76,900 kilos × $6.00 per kilo)
= $469,090 − $461,400
= $7,690 Unfavorable
c. Standard hours = 8,400 units × 0.4 hours per unit = 3,360 hours
Labor efficiency variance = (Actual hours − Standard hours) × Standard rate
= (3,320 hours − 3,360 hours) × $11.00 per hour
= (−40 hours) × $11.00 per hour
= $440 Favorable
d. Labor rate variance = (Actual hours × Actual rate) − (Actual hours × Standard rate)
= ($35,524) − (3,320 hours × $11.00 per hour)
= $35,524 − $36,520
= $996 Favorable
e. Standard hours = 8,400 units × 0.4 hours per unit = 3,360 hours
Variable overhead efficiency variance = (Actual hours − Standard hours) × Standard rate
= (3,320 hours − 3,360 hours) × $5.00 per hour
= (−40 hours) × $5.00 per hour
= $200 Favorable
f. Variable overhead rate variance = (Actual hours × Actual rate) − (Actual hours × Standard rate)
= ($17,928) − (3,320 hours × $5.00 per hour)
= $17,928 − $16,600
= $1,328 Unfavorable
Materials quantity variance = (Actual quantity − Standard quantity) × Standard price
= (71,750 kilos − 72,240 kilos) × $6.00 per kilo
= (−490 kilos) × $6.00 per kilo
= $2,940 Favorable
b. Materials price variance = (Actual quantity × Actual price) − (Actual quantity × Standard price)
= ($469,090) − (76,900 kilos × $6.00 per kilo)
= $469,090 − $461,400
= $7,690 Unfavorable
c. Standard hours = 8,400 units × 0.4 hours per unit = 3,360 hours
Labor efficiency variance = (Actual hours − Standard hours) × Standard rate
= (3,320 hours − 3,360 hours) × $11.00 per hour
= (−40 hours) × $11.00 per hour
= $440 Favorable
d. Labor rate variance = (Actual hours × Actual rate) − (Actual hours × Standard rate)
= ($35,524) − (3,320 hours × $11.00 per hour)
= $35,524 − $36,520
= $996 Favorable
e. Standard hours = 8,400 units × 0.4 hours per unit = 3,360 hours
Variable overhead efficiency variance = (Actual hours − Standard hours) × Standard rate
= (3,320 hours − 3,360 hours) × $5.00 per hour
= (−40 hours) × $5.00 per hour
= $200 Favorable
f. Variable overhead rate variance = (Actual hours × Actual rate) − (Actual hours × Standard rate)
= ($17,928) − (3,320 hours × $5.00 per hour)
= $17,928 − $16,600
= $1,328 Unfavorable

Learning Objectives
- Calculate variances between actual and standard costs for direct materials and direct labor.
- Investigate and interpret the differential in materials' pricing and volume.
- Execute computation and detailed explanation of direct labor rate and efficiency discrepancies.