Asked by Emily Maniccia on May 30, 2024

Verified
Tulip Company produces two products, T and U. The indirect labor costs include the following two items:  The following activity-base usage and unit production information is available for the two products:
The following activity-base usage and unit production information is available for the two products: 
a.Determine the single plantwide factory overhead rate, using direct labor hours as the activity base.
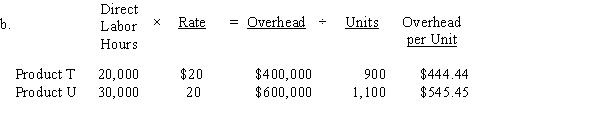
b.Determine the factory overhead allocated per unit for Products T and U, using the single plantwide factory overhead rate.
c.Determine the activity rate for plant supervision and setup labor, assuming that the activity base for supervision is direct labor hours and the activity base for setup labor is number of setups.
d.Determine the factory overhead allocated per unit for Products T and U, using the activity-based costing method.
e.Why is the factory overhead allocated per unit different for the two products under the two methods?
Plantwide Factory Overhead Rate
A single overhead absorption rate used throughout an entire plant or factory to allocate overhead costs to products.
Activity-based Costing
An accounting method that assigns costs to products and services based on the activities and resources that go into creating them, aiming for more accurate costing.
Indirect Labor Costs
Costs related to labor that cannot be directly tied to the production of specific goods or services, such as maintenance personnel or supervisors.
- Comprehend the computation and utilization of a unified plantwide manufacturing overhead rate determined by direct labor hours.
- Engage in activity-based costing practices to allocate indirect costs among different products or services.
- Compute and analyze the allocation of factory overhead per unit utilizing various costing techniques.

Verified Answer
= $1,000,000 ÷ 50,000 dlh
= $20 per dlh

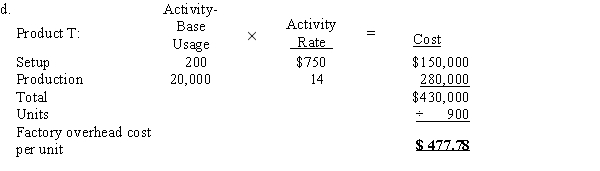
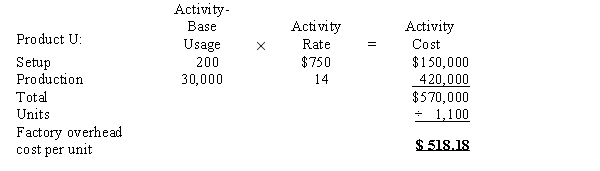 e.The factory overhead cost per unit under the single plantwide rate method is distorted because Product U consumes more setup-related activity relative to the amount of direct labor consumed than does Product T. Thus, the activity-based costing method, which separates setup according to its own activity base, provides a more accurate estimate of the factory overhead cost per unit.
e.The factory overhead cost per unit under the single plantwide rate method is distorted because Product U consumes more setup-related activity relative to the amount of direct labor consumed than does Product T. Thus, the activity-based costing method, which separates setup according to its own activity base, provides a more accurate estimate of the factory overhead cost per unit.
Learning Objectives
- Comprehend the computation and utilization of a unified plantwide manufacturing overhead rate determined by direct labor hours.
- Engage in activity-based costing practices to allocate indirect costs among different products or services.
- Compute and analyze the allocation of factory overhead per unit utilizing various costing techniques.
Related questions
Valhalla Company Manufactures Small Table Lamps and Desk Lamps ...
Condoleezza Co ...
Pikes Peak Leather Company Manufactures Leather Handbags and Moccasins ...
Beckley Corporation Has Provided the Following Data from Its Activity-Based ...
Howell Corporation's Activity-Based Costing System Has Three Activity Cost Pools--Machining ...