Asked by Kelsey Whalen on Jun 11, 2024

Verified
Sarah's Pretzel plant has the following short-run cost function: 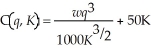 where q is Sarah's output level, w is the cost of a labor hour, and K is the number of pretzel machines Sarah leases. Sarah's short-run marginal cost curve is
where q is Sarah's output level, w is the cost of a labor hour, and K is the number of pretzel machines Sarah leases. Sarah's short-run marginal cost curve is 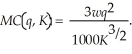 At the moment, Sarah leases 10 pretzel machines, the cost of a labor hour is $6.85, and she can sell all the output she produces at $35 per unit. If the cost per labor hour rises to $7.50, what happens to Sarah's optimal level of output and profits?
At the moment, Sarah leases 10 pretzel machines, the cost of a labor hour is $6.85, and she can sell all the output she produces at $35 per unit. If the cost per labor hour rises to $7.50, what happens to Sarah's optimal level of output and profits?
Short-Run Marginal Cost Curve
A graph that shows the cost of producing one more unit of a good or service in the short term, when some factors of production are fixed.
Optimal Level
The most efficient, effective, or desirable point or degree in a process, situation, or system.
Leases
Legal agreements that allow for the use of property or equipment for a specified time in exchange for payment.
- Examine the influence of changing input expenses on an enterprise's output and strategies for achieving maximum profitability in a perfectly competitive environment.
- Identify the optimum production quantity, gain, or loss through evaluation of cost functions and market price points.

Verified Answer
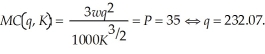 The average variable cost at this output level is:
The average variable cost at this output level is: 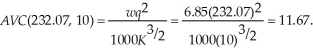 Since
Since 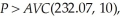 Sarah will maximize profits at 232.07 units. Sarah's profits are:
Sarah will maximize profits at 232.07 units. Sarah's profits are: 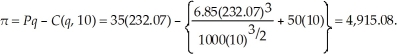 To determine the optimal output level at the higher wage rate, we need to first equate marginal cost to the market price. That is,
To determine the optimal output level at the higher wage rate, we need to first equate marginal cost to the market price. That is, 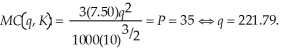 The average variable cost at this output level is:
The average variable cost at this output level is: 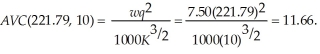 Since
Since 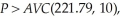 Sarah will maximize profits at 221.79 units. Sarah's profits are:
Sarah will maximize profits at 221.79 units. Sarah's profits are: 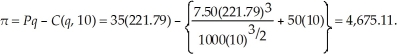 The higher wage rate causes Sarah to reduce output and her profits also fall. In this case, profits fall by 4.9% when the wage rate rises by 9.5%.
The higher wage rate causes Sarah to reduce output and her profits also fall. In this case, profits fall by 4.9% when the wage rate rises by 9.5%.
Learning Objectives
- Examine the influence of changing input expenses on an enterprise's output and strategies for achieving maximum profitability in a perfectly competitive environment.
- Identify the optimum production quantity, gain, or loss through evaluation of cost functions and market price points.
Related questions
Ronny's Pizza House Operates in the Perfectly Competitive Local Pizza ...
Assume the Market for Tortillas Is Perfectly Competitive ...
Homer's Boat Manufacturing Cost Function Is: the Marginal Cost ...
The Market for Wheat Consists of 500 Identical Firms, Each ...
Consider a Competitive Market in Which the Market Demand for ...