Asked by MATTANAPORN CHANTIYANON on Apr 27, 2024

Verified
Consider a competitive market in which the market demand for the product is expressed as
P = 75 - 1.5Q,
and the supply of the product is expressed as
P = 25 + 0.50Q.
Price, P, is in dollars per unit sold, and Q represents rate of production and sales in hundreds of units per day. The typical firm in this market has a marginal cost of
MC = 2.5 + 10q.
a. Determine the equilibrium market price and rate of sales.
b. Determine the rate of sales of the typical firm, given your answer to part (a) above.
c. If the market demand were to increase to 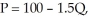 what would the new price and rate of sales in the market be? What would the new rate of sales for the typical firm be?
what would the new price and rate of sales in the market be? What would the new rate of sales for the typical firm be?
d. If the original supply and demand represented a long-run equilibrium condition in the market, would the new equilibrium (c) represent a new long-run equilibrium for the typical firm? Explain.
Market Demand
The total quantity of a product or service that all consumers in a market are willing and able to purchase at various prices.
Marginal Cost
The cost of producing an additional unit of output, highlighting the concept of increasing or decreasing returns.
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity of a good or service demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers, leading to market stability.
- Identify the supreme output, cost efficiency, and profitability for firms subjected to different market environments.
- Assess the role of supply and demand in determining market equilibrium prices and quantities.
- Identify factors that influence firm entry and exit in competitive markets.

Verified Answer
2Q = 50
Q = 25 (hundreds per day)
The equilibrium price is
P = 75 - 1.5Q
= 75 - 1.5(25)
= $37.5
b.Since the firm's supply curve is its MC, we can determine the rate of sales of the firm by inserting $37.5 for price (MC) into the MC equation to get q for the firm.
MC = $37.5 = 2.5 + 10q.
q = 3.5 (hundreds per day)
c.The new market equilibrium price is
25 + 0.50Q = 100 - 1.5Q
Q = 75 / 2 (hundreds per day)
P = 100 - 1.5(37.5) = $43.75 / unit
Now the typical firm would sell daily:
MC = 43.75 = 2.5 + 10q
q = 4.126 (hundred per day)
d.The original supply and demand represented long-run equilibrium and a breakeven situation for the typical firm. With the new higher demand in (c), the typical firm would likely be earning a positive economic profit because price and output are both higher. This apparent positive profit would encourage more firms to enter the market, which would increase market supply. So, the new equilibrium would not represent a long-run equilibrium for the firm or the market.

Learning Objectives
- Identify the supreme output, cost efficiency, and profitability for firms subjected to different market environments.
- Assess the role of supply and demand in determining market equilibrium prices and quantities.
- Identify factors that influence firm entry and exit in competitive markets.
Related questions
Bud Owen Operates Bud's Package Store in a Small College ...
If a Firm in a Perfectly Competitive Industry Is Experiencing ...
When the Supply of 35 Mm Cameras Increases,the New Market ...
Assume the Market for Tortillas Is Perfectly Competitive ...
Homer's Boat Manufacturing Cost Function Is: the Marginal Cost ...