Asked by Amanda Rettenmaier on Jun 11, 2024

Verified
The market for wheat consists of 500 identical firms, each with the total and marginal cost functions shown:
TC = 90,000 + 0.00001Q2
MC = 0.00002Q,
where Q is measured in bushels per year. The market demand curve for wheat is Q = 90,000,000 20,000,000P, where Q is again measured in bushels and P is the price per bushel.
a. Determine the short-run equilibrium price and quantity that would exist in the market.
b. Calculate the profit maximizing quantity for the individual firm. Calculate the firm's short-run profit (loss) at that quantity.
c. Assume that the short-run profit or loss is representative of the current long-run prospects in this market. You may further assume that there are no barriers to entry or exit in the market. Describe the expected long-run response to the conditions described in part b. (The TC function for the firm may be regarded as an economic cost function that captures all implicit and explicit costs.)
Short-Run Equilibrium
The condition in which market supply equals market demand within a short time frame, establishing a temporary market price.
Marginal Cost Functions
Represents the change in total cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented by one unit.
- Determine the best outcome, earnings, or deficits from analyzing cost structures and pricing in the marketplace.
- Ascertain the balance of market output, individual firm output, and the profit or deficit in a competitive market environment.
- Examine the impact of outside influences like taxation on supply and the behavior of markets.

Verified Answer
PM
Patrick MensahJun 13, 2024
Final Answer :
a.Market supply is horizontal sum of individual firm supply (firm's MC curve).
Firm's TC = 90,000 + 0.00001Q2
MC = 0.00002Q = P.
Solve for Q in terms of P to express as supply curve
P = 0.00002Q
Q = 50,000P
Market supply curve is horizontal sum of firm supply curve or N-times the firm supply curve (N is the number of firms).
QS = 500(50,000)P
QS = 25,000,000P
Equate QS and QD to determine price and quantity.
25,000,000P = 90,000,000 - 20,000,000P
45,000,000P = 90,000,000
P = $2.00
Q = 25,000,000P
Q = 25,000,000(2)
Q = 50,000,000
b.To determine the firm's output, equate price and marginal cost - Firm's MC = 0.00002Q.
P = 2 = 0.00002Q
Q = 100,000
Firm's π = TR - TC
TR = 2.00(100,000)
TR = 200,000
TC = 90,000 +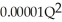 TC = 90,000 +
TC = 90,000 + 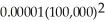 TC = 190,000
TC = 190,000
π = 200,000,000 - 190,000 = 10,000
c.Firms are earning economic profit so we would expect entry to occur, causing the market supply curve to shift rightward. As the market supply curve shifts rightward, price falls, which in turn causes each firm to reduce its output. This will continue until we reach long-run equilibrium at zero profit.
Firm's TC = 90,000 + 0.00001Q2
MC = 0.00002Q = P.
Solve for Q in terms of P to express as supply curve
P = 0.00002Q
Q = 50,000P
Market supply curve is horizontal sum of firm supply curve or N-times the firm supply curve (N is the number of firms).
QS = 500(50,000)P
QS = 25,000,000P
Equate QS and QD to determine price and quantity.
25,000,000P = 90,000,000 - 20,000,000P
45,000,000P = 90,000,000
P = $2.00
Q = 25,000,000P
Q = 25,000,000(2)
Q = 50,000,000
b.To determine the firm's output, equate price and marginal cost - Firm's MC = 0.00002Q.
P = 2 = 0.00002Q
Q = 100,000
Firm's π = TR - TC
TR = 2.00(100,000)
TR = 200,000
TC = 90,000 +
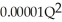 TC = 90,000 +
TC = 90,000 + 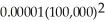 TC = 190,000
TC = 190,000π = 200,000,000 - 190,000 = 10,000
c.Firms are earning economic profit so we would expect entry to occur, causing the market supply curve to shift rightward. As the market supply curve shifts rightward, price falls, which in turn causes each firm to reduce its output. This will continue until we reach long-run equilibrium at zero profit.

Learning Objectives
- Determine the best outcome, earnings, or deficits from analyzing cost structures and pricing in the marketplace.
- Ascertain the balance of market output, individual firm output, and the profit or deficit in a competitive market environment.
- Examine the impact of outside influences like taxation on supply and the behavior of markets.