Asked by Isabella Pucci on May 07, 2024

Verified
Project A requires an original investment of $50,000. The project will yield cash flows of $15,000 per year for 7 years. Project B has a computed net present value of $13,500 over a 4-year life. Project A could be sold at the end of 4 years for $25,000. (a) Using the present value tables that follow, determine the net present value of Project A over a 4-year life with salvage value assuming a minimum rate of return of 12%. (b) Which project provides the greatest net present value?
Following is a table for the present value of $1 at compound interest: 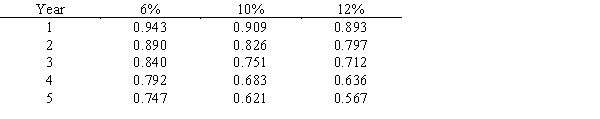 Following is a table for the present value of an annuity of $1 at compound interest:
Following is a table for the present value of an annuity of $1 at compound interest: 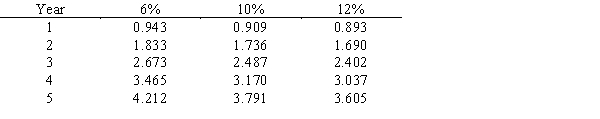
Present Value Tables
Tables utilized in finance to determine the present value of a sum that will be received at a future date by applying a specific discount rate.
Original Investment
The initial amount of money put into a project, asset, or business, used as a basis for determining future returns or profitability.
Salvage Value
An alternative term for residual value, referring to the estimated resale value of an asset at the end of its useful life.
- Acquire knowledge about the concept and relevance of Net Present Value (NPV) in the appraisal of capital investments.
- Acquire the ability to compute the Net Present Value of different investment proposals by applying present value factors.
- Capability to evaluate and differentiate between various investment options in capital using calculations of Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR).

Verified Answer
NS
Noxolo StellaMay 13, 2024
Final Answer :
a. 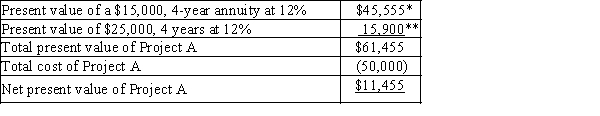 *$15,000 × 3.037 (present value of an annuity of $1 at 12% for 4 years)**$25,000 × 0.636 (present value of $1 at 12% for 4 years)b. Project B's present value of $13,500 is greater than the net present value of Project A of $11,455.
*$15,000 × 3.037 (present value of an annuity of $1 at 12% for 4 years)**$25,000 × 0.636 (present value of $1 at 12% for 4 years)b. Project B's present value of $13,500 is greater than the net present value of Project A of $11,455.
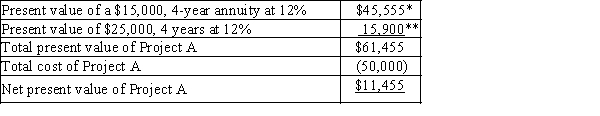 *$15,000 × 3.037 (present value of an annuity of $1 at 12% for 4 years)**$25,000 × 0.636 (present value of $1 at 12% for 4 years)b. Project B's present value of $13,500 is greater than the net present value of Project A of $11,455.
*$15,000 × 3.037 (present value of an annuity of $1 at 12% for 4 years)**$25,000 × 0.636 (present value of $1 at 12% for 4 years)b. Project B's present value of $13,500 is greater than the net present value of Project A of $11,455.
Learning Objectives
- Acquire knowledge about the concept and relevance of Net Present Value (NPV) in the appraisal of capital investments.
- Acquire the ability to compute the Net Present Value of different investment proposals by applying present value factors.
- Capability to evaluate and differentiate between various investment options in capital using calculations of Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR).