Asked by Himani Patel on May 22, 2024

Verified
Lakatos Corporation manufactures one product. It does not maintain any beginning or ending Work in Process inventories. The company uses a standard cost system in which inventories are recorded at their standard costs. There is no variable manufacturing overhead. The standard cost card for the company's only product contains the following information concerning direct materials: 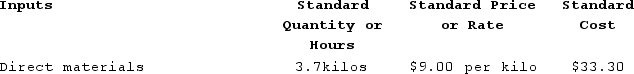 During the year, the company completed the following transactions concerning direct materials:a. Purchased 151,800 kilos of raw material at a price of $9.70 per kilo.b. Used 140,870 kilos of the raw material to produce 38,100 units of work in process.The company calculated the following direct materials variances for the year:
During the year, the company completed the following transactions concerning direct materials:a. Purchased 151,800 kilos of raw material at a price of $9.70 per kilo.b. Used 140,870 kilos of the raw material to produce 38,100 units of work in process.The company calculated the following direct materials variances for the year:
 Assume that all transactions are recorded on the below worksheet, which is similar to the worksheet shown in your text except that it has been divided into two parts so that it fits on one page. The beginning balances in each of the accounts have been given. PP&E (net) stands for Property, Plant, and Equipment net of depreciation.
Assume that all transactions are recorded on the below worksheet, which is similar to the worksheet shown in your text except that it has been divided into two parts so that it fits on one page. The beginning balances in each of the accounts have been given. PP&E (net) stands for Property, Plant, and Equipment net of depreciation.
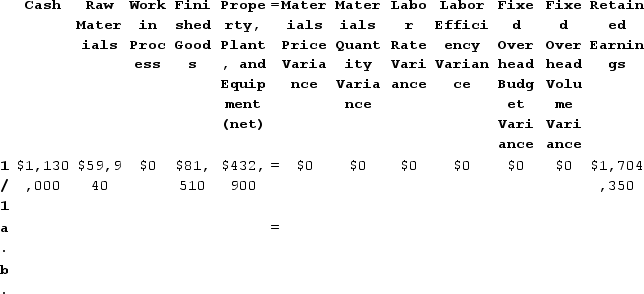 When the raw materials used in production are recorded in transaction (b) above, which of the following entries will be made?
When the raw materials used in production are recorded in transaction (b) above, which of the following entries will be made?
A) ($900) in the Materials Quantity Variance column
B) ($900) in the Materials Price Variance column
C) $900 in the Materials Price Variance column
D) $900 in the Materials Quantity Variance column
Materials Quantity Variance
The difference between the actual quantity of materials used in production and the expected (or standard) quantity, measured in financial terms.
Direct Materials
These are the raw materials that are directly incorporated into a finished product.
Standard Cost Card
A document that lists the standard costs associated with producing a single unit of a product, including materials, labor, and overhead.
- Calculate and investigate variations from conventional cost standards, implicating discrepancies in the cost of materials, deviations in the volume of materials, wage rate variances, productivity variances in labor, fixed overhead budgetary differences, and fixed overhead capacity discrepancies.

Verified Answer
HE
Helmy EissaMay 25, 2024
Final Answer :
D
Explanation :
The standard cost per kilo of raw material is $9, and the actual cost per kilo is $9.70. Therefore, there is an unfavorable price variance of $0.70 per kilo ($9.70 actual cost - $9 standard cost). The company used 140,870 kilos of raw material, which is less than the standard quantity allowed for the 38,100 units of work in process (38,100 units × 4 kilos per unit = 152,400 kilos). Therefore, there is a favorable quantity variance of 530 kilos (152,400 standard quantity allowed - 140,870 actual quantity used). The total direct materials variance is the sum of the price and quantity variances, which is an unfavorable variance of $372,900 ($0.70 unfavorable price variance × 140,870 actual quantity used - $0.013986 favorable quantity variance per kilo × 140,870 actual quantity used = $98,413.90 unfavorable price variance + $274,486.10 favorable quantity variance = $372,900 unfavorable total variance). When the raw materials used in production are recorded, the entry will be a credit to Raw Materials Inventory for the actual cost of the raw materials used ($1,370,109 = 140,870 kilos × $9.70 per kilo) and a debit to Work in Process Inventory for the standard cost of the raw materials used ($1,370,109 = 140,870 kilos × $9.70 per kilo). The difference between the actual cost and the standard cost of the raw materials used ($372,900 unfavorable variance) is recorded as a debit to the Materials Quantity Variance account and an equal credit to the Materials Price Variance account. Therefore, the answer is choice D ($900 in the Materials Quantity Variance column).

Learning Objectives
- Calculate and investigate variations from conventional cost standards, implicating discrepancies in the cost of materials, deviations in the volume of materials, wage rate variances, productivity variances in labor, fixed overhead budgetary differences, and fixed overhead capacity discrepancies.