Asked by Kalindi Schneider on Apr 26, 2024

Verified
In the long-run equilibrium of a competitive market, the market supply and demand are:
Supply: P = 30 + 0.50Q
Demand: P = 100 - 1.5Q,
where P is dollars per unit and Q is rate of production and sales in hundreds of units per day. A typical firm in this market has a marginal cost of production expressed as:
MC = 3.0 + 15q.
a. Determine the market equilibrium rate of sales and price.
b. Determine the rate of sales by the typical firm.
c. Determine the economic rent that the typical firm enjoys. (Hint: Note that the marginal cost function is linear.)
d. If an output tax is imposed on ONE firm's output such that the ONE firm has a new marginal cost (including the tax) of: 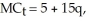 what will the firm's new rate of production be after the tax is imposed? How does this new production rate compare with the pre-tax rate? Is it as expected? Explain. Would the effect have been the same if the tax had been imposed on all firms equally? Explain.
what will the firm's new rate of production be after the tax is imposed? How does this new production rate compare with the pre-tax rate? Is it as expected? Explain. Would the effect have been the same if the tax had been imposed on all firms equally? Explain.
Market Supply And Demand
The economic model that explains the interaction between the supply of goods and services and the demand for them, determining their market prices.
Marginal Cost
A rise in the cumulative expenses associated with the production of an extra unit.
Economic Rent
Extra income earned by a factor of production due to its limited supply or unique properties, over and above its opportunity cost.
- Utilize understanding of cost functions to determine the best output level and comprehend its impact on a company's profit margins.
- Comprehend how taxation and regulatory measures influence a corporation's long-term production choices and economic results.

Verified Answer
Supply = Demand
30 + 0.50Q = 100 - 1.5Q
Q = 70/2 = 35 (hundred per day)
P = 30 + 0.50(35) = $47.5 / unit
b.The rate of sales by the typical firm is determined from the firm's MC curve.MC = 47.5 = 3 + 15q
q = 2.967 (hundred per day)
c.The economic rent that the firm earns in the long-run is equal to the producer surplus that it generates. The producer surplus is the area of the triangle bounded by price, MC, and production rate, a triangle.P = 47.5 q = 2.833 MC (lower point) = 3
Economic rent = (1/2)b ∙ h = (0.5)(2.967)(47.5 - 3)
= $66.016 (hundreds)
d.The market price is expected to stay the same since the tax is imposed on the one firm. Thus, the production rate for the firm is determined at the intersection of price and MCt of the firm.
47.5 = 5 + 15q
q = 2.833 (hundreds of units per day)
This production rate is slightly less than the pre-tax rate, as expected. The tax had the effect of shifting the MC curve vertically upward. This resulted in an intersection with the price line at 2.833 instead of 2.967.
The effect would not have been the same if the tax had been imposed equally on all firms. With the tax on all firms, the equilibrium market price would have increased. The industry supply curve would have shifted upward and total industry output would have decreased. Instead of the one firm being affected with one firm being taxed, the industry equilibrium price and output would be affected when the tax was imposed on all firms.

Learning Objectives
- Utilize understanding of cost functions to determine the best output level and comprehend its impact on a company's profit margins.
- Comprehend how taxation and regulatory measures influence a corporation's long-term production choices and economic results.
Related questions
The Long-Run Cost Function for LeAnn's Telecommunication Firm Is ...
The Long-Run Cost Function for Jeremy's Jetski Rentals Is ...
Homer's Boat Manufacturing Cost Function Is: the Marginal Cost ...
Assume the Market for Tortillas Is Perfectly Competitive ...
The Market for Wheat Consists of 500 Identical Firms, Each ...