Asked by Javier Lopez on Jun 16, 2024

Verified
The long-run cost function for LeAnn's telecommunication firm is: 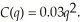 A local telecommunication tax of $0.01 has been implemented for each unit LeAnn sells. This implies the marginal cost function becomes:
A local telecommunication tax of $0.01 has been implemented for each unit LeAnn sells. This implies the marginal cost function becomes: 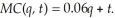 If LeAnn can sell all the units she produces at the market price of $0.70, calculate LeAnn's optimal output before and after the tax. What effect did the tax have on LeAnn's output level? How did LeAnn's profits change?
If LeAnn can sell all the units she produces at the market price of $0.70, calculate LeAnn's optimal output before and after the tax. What effect did the tax have on LeAnn's output level? How did LeAnn's profits change?
Long-Run Cost Function
A relationship that shows the lowest cost at which a firm can produce any given level of output in the long run, where all inputs are variable.
Marginal Cost Function
is a mathematical representation that shows how the cost of producing one additional unit of a good varies as the quantity of production changes.
Telecommunication Tax
Taxes that are applied specifically to telecommunication services provided to consumers, including telephone and internet services.
- Gain an insight into the impact of legislative frameworks and tax obligations on the production strategies and financial performance of enterprises over an extended period.

Verified Answer
DG
Dinah GaspardJun 17, 2024
Final Answer :
The profit maximizing output level is where the market price equals marginal cost (providing the price exceeds the average variable cost). To determine the optimal output level, we need to first equate marginal cost to the market price. That is, 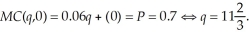 The average variable cost at this output level is:
The average variable cost at this output level is: 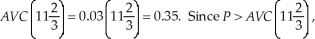 LeAnn will maximize profits at
LeAnn will maximize profits at 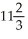 units. LeAnn's profits are:
units. LeAnn's profits are: 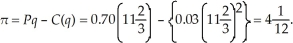 With the tax, LeAnn's optimal output level requires:
With the tax, LeAnn's optimal output level requires: 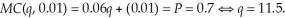 The average variable cost at this output level is:
The average variable cost at this output level is: 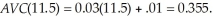 Since
Since 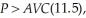 LeAnn will maximize profits at 11.5 units. LeAnn's profit with the tax is:
LeAnn will maximize profits at 11.5 units. LeAnn's profit with the tax is: 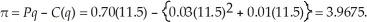 The tax reduces LeAnn's output and profit.
The tax reduces LeAnn's output and profit.
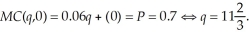 The average variable cost at this output level is:
The average variable cost at this output level is: 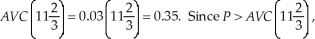 LeAnn will maximize profits at
LeAnn will maximize profits at 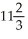 units. LeAnn's profits are:
units. LeAnn's profits are: 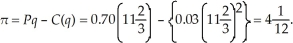 With the tax, LeAnn's optimal output level requires:
With the tax, LeAnn's optimal output level requires: 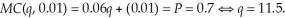 The average variable cost at this output level is:
The average variable cost at this output level is: 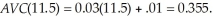 Since
Since 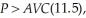 LeAnn will maximize profits at 11.5 units. LeAnn's profit with the tax is:
LeAnn will maximize profits at 11.5 units. LeAnn's profit with the tax is: 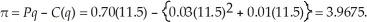 The tax reduces LeAnn's output and profit.
The tax reduces LeAnn's output and profit.
Learning Objectives
- Gain an insight into the impact of legislative frameworks and tax obligations on the production strategies and financial performance of enterprises over an extended period.