Asked by JOSHUA MILLER on May 12, 2024

Verified
Gathman Corporation manufactures one product. It does not maintain any beginning or ending Work in Process inventories. The company uses a standard cost system in which inventories are recorded at their standard costs and any variances are closed directly to Cost of Goods Sold. There is no variable manufacturing overhead. The company's balance sheet at the beginning of the year was as follows:
 The standard cost card for the company's only product is as follows:
The standard cost card for the company's only product is as follows:
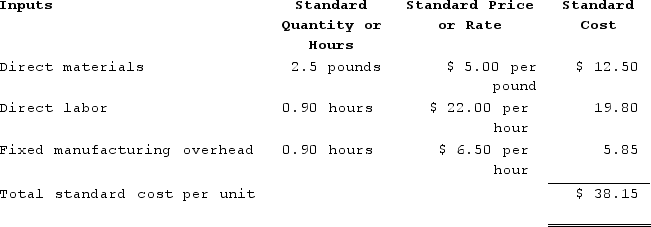 The standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate was based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $117,000 and budgeted activity of 18,000 hours.During the year, the company completed the following transactions:Purchased 36,300 pounds of raw material at a price of $4.70 per pound.Used 32,100 pounds of the raw material to produce 12,800 units of work in process.Assigned direct labor costs to work in process. The direct labor workers (who were paid in cash) worked 12,520 hours at an average cost of $21.00 per hour.Applied fixed overhead to the 12,800 units in work in process inventory using the predetermined overhead rate multiplied by the number of direct labor-hours allowed. Actual fixed overhead costs for the year were $132,700. Of this total, $27,700 related to items such as insurance, utilities, and indirect labor salaries that were all paid in cash and $105,000 related to depreciation of manufacturing equipment.Transferred 12,800 units from work in process to finished goods.Sold for cash 12,600 units to customers at a price of $52.10 per unit.Completed and transferred the standard cost associated with the 12,600 units sold from finished goods to cost of goods sold.Paid $73,000 of selling and administrative expenses.Closed all standard cost variances to cost of goods sold.Required:1. Compute all direct materials, direct labor, and fixed overhead variances for the year.2. Enter the beginning balances and record the above transactions in the worksheet that appears below. Because of the width of the worksheet, it is in two parts. In your text, these two parts would be joined side-by-side to make one very wide worksheet.
The standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate was based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $117,000 and budgeted activity of 18,000 hours.During the year, the company completed the following transactions:Purchased 36,300 pounds of raw material at a price of $4.70 per pound.Used 32,100 pounds of the raw material to produce 12,800 units of work in process.Assigned direct labor costs to work in process. The direct labor workers (who were paid in cash) worked 12,520 hours at an average cost of $21.00 per hour.Applied fixed overhead to the 12,800 units in work in process inventory using the predetermined overhead rate multiplied by the number of direct labor-hours allowed. Actual fixed overhead costs for the year were $132,700. Of this total, $27,700 related to items such as insurance, utilities, and indirect labor salaries that were all paid in cash and $105,000 related to depreciation of manufacturing equipment.Transferred 12,800 units from work in process to finished goods.Sold for cash 12,600 units to customers at a price of $52.10 per unit.Completed and transferred the standard cost associated with the 12,600 units sold from finished goods to cost of goods sold.Paid $73,000 of selling and administrative expenses.Closed all standard cost variances to cost of goods sold.Required:1. Compute all direct materials, direct labor, and fixed overhead variances for the year.2. Enter the beginning balances and record the above transactions in the worksheet that appears below. Because of the width of the worksheet, it is in two parts. In your text, these two parts would be joined side-by-side to make one very wide worksheet.
 3. Determine the ending balance (e.g., 12/31 balance) in each account.4. Prepare an income statement for the year.
3. Determine the ending balance (e.g., 12/31 balance) in each account.4. Prepare an income statement for the year.
Direct Labor
The labor costs that can be directly attributed to the production of goods or services, such as wages for workers who manufacture a product.
Work in Process
Inventory that includes goods partially through the manufacturing process but not yet completed.
- Understand the process of accurately logging transactions in a standard costing system.
- Develop the skill to determine the differences between actual expenditures and normative costs, including variations in direct materials, direct labor, and fixed overhead.
- Understand the process of preparing and analyzing income statements for manufacturing companies through standard costing techniques.

Verified Answer
SL
Shannon LamarMay 19, 2024
Final Answer :
1.Materials price variance = Actual quantity × (Actual price − Standard price)= 36,300 pounds × ($4.70 per pound − $5.00 per pound)= 36,300 pounds × (−$0.30 per pound)= $10,890 FavorableMaterials quantity variance:Standard quantity = Actual output × Standard quantity = 12,800 units × 2.5 pounds per unit = 32,000 poundsMaterials quantity variance = (Actual quantity − Standard quantity) × Standard price= (32,100 pounds − 32,000 pounds) × $5.00 per pound= (100 pounds) × $5.00 per pound= $500 UnfavorableLabor rate variance = Actual hours × (Actual rate − Standard rate)= 12,520 hours × ($21.00 per hour − $22.00 per hour)= 12,520 hours × (−$1.00 per hour)= $12,520 FavorableLabor efficiency variance:Standard hours = Actual output × Standard quantity = 12,800 units × 0.90 hours per unit = 11,520 hoursLabor efficiency variance = (Actual hours − Standard hour) × Standard rate= (12,520 hours − 11,520 hours) × $22.00 per hour= (1,000 hours) × $22.00 per hour= $22,000 UnfavorableBudget variance = Actual fixed overhead − Budgeted fixed overhead= $132,700 − $117,000= $15,700 UnfavorableVolume variance = Budgeted fixed overhead − Fixed overhead applied to work in process= $117,000 − (11,520 hours × $6.50 per hour)= $117,000 − ($74,880)= $42,120 Unfavorable2. and 3.
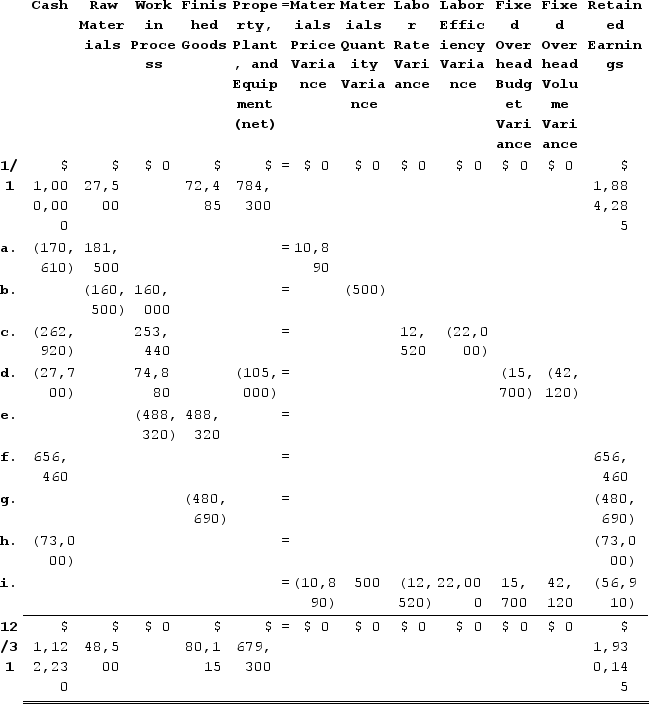 The explanations for transactions a through i are as follows:Cash decreases by the actual cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Actual price = 36,300 pounds × $4.70 per pound = $170,610. Raw Materials increase by the standard cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 36,300 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $181,500. The materials price variance is $10,890 Favorable.Raw Materials decrease by the standard cost of the raw materials used in production, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 32,100 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $160,500. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard quantity of raw materials allowed for the actual output, which is Standard quantity × Standard price = (12,800 units × 2.5 pounds per unit) × $5.00 per pound = 32,000 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $160,000. The difference is the Materials Quantity Variance which is $500 Unfavorable.Cash decreases by the actual amount paid to direct laborers, which is Actual hours × Actual rate = 12,520 hours × $21.00 per hour = $262,920. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output, which is Standard hours × Standard rate = (12,800 units × 0.90 hours per unit) × $22.00 per hour = 11,520 hours × $22.00 per hour = $253,440. The difference consists of the Labor Rate Variance which is $12,520 Favorable and the Labor Efficiency Variance which is $22,000 Unfavorable.Cash decreases by the actual amount paid for various fixed overhead costs, which is $27,700. Work in Process increases by the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output multiplied by the predetermined overhead rate, which is (12,800 units × 0.90 hours per unit) × $6.50 per hour = 11,520 hours × $6.50 per hour = $74,880. Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) decreases by the amount of depreciation for the period, which is $105,000. The difference is the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Budget Variance which is $15,700 Unfavorable and the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Volume Variance which is $42,120 Unfavorable.Work in Process decreases by the number of units transferred to Finished Goods multiplied by the standard cost per unit = 12,800 units × $38.15 per unit = $488,320. Finished Goods increases by the same amount.Cash increases by the number of units sold multiplied by the selling price per unit, which is 12,600 units × $52.10 per unit = $656,460. Retained Earnings increases by the same amount.Finished Goods decreases by the number of units sold multiplied by their standard cost per unit, which is 12,600 units × $38.15 per unit = $480,690. Retained Earnings decreases by the same amount.Cash and Retained Earnings decrease by $73,000 to record the selling and administrative expenses.All variance accounts take their balance to zero and they are closed to Cost of Goods Sold (which resides within Retained Earnings).4.
The explanations for transactions a through i are as follows:Cash decreases by the actual cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Actual price = 36,300 pounds × $4.70 per pound = $170,610. Raw Materials increase by the standard cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 36,300 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $181,500. The materials price variance is $10,890 Favorable.Raw Materials decrease by the standard cost of the raw materials used in production, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 32,100 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $160,500. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard quantity of raw materials allowed for the actual output, which is Standard quantity × Standard price = (12,800 units × 2.5 pounds per unit) × $5.00 per pound = 32,000 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $160,000. The difference is the Materials Quantity Variance which is $500 Unfavorable.Cash decreases by the actual amount paid to direct laborers, which is Actual hours × Actual rate = 12,520 hours × $21.00 per hour = $262,920. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output, which is Standard hours × Standard rate = (12,800 units × 0.90 hours per unit) × $22.00 per hour = 11,520 hours × $22.00 per hour = $253,440. The difference consists of the Labor Rate Variance which is $12,520 Favorable and the Labor Efficiency Variance which is $22,000 Unfavorable.Cash decreases by the actual amount paid for various fixed overhead costs, which is $27,700. Work in Process increases by the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output multiplied by the predetermined overhead rate, which is (12,800 units × 0.90 hours per unit) × $6.50 per hour = 11,520 hours × $6.50 per hour = $74,880. Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) decreases by the amount of depreciation for the period, which is $105,000. The difference is the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Budget Variance which is $15,700 Unfavorable and the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Volume Variance which is $42,120 Unfavorable.Work in Process decreases by the number of units transferred to Finished Goods multiplied by the standard cost per unit = 12,800 units × $38.15 per unit = $488,320. Finished Goods increases by the same amount.Cash increases by the number of units sold multiplied by the selling price per unit, which is 12,600 units × $52.10 per unit = $656,460. Retained Earnings increases by the same amount.Finished Goods decreases by the number of units sold multiplied by their standard cost per unit, which is 12,600 units × $38.15 per unit = $480,690. Retained Earnings decreases by the same amount.Cash and Retained Earnings decrease by $73,000 to record the selling and administrative expenses.All variance accounts take their balance to zero and they are closed to Cost of Goods Sold (which resides within Retained Earnings).4.

 The explanations for transactions a through i are as follows:Cash decreases by the actual cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Actual price = 36,300 pounds × $4.70 per pound = $170,610. Raw Materials increase by the standard cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 36,300 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $181,500. The materials price variance is $10,890 Favorable.Raw Materials decrease by the standard cost of the raw materials used in production, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 32,100 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $160,500. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard quantity of raw materials allowed for the actual output, which is Standard quantity × Standard price = (12,800 units × 2.5 pounds per unit) × $5.00 per pound = 32,000 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $160,000. The difference is the Materials Quantity Variance which is $500 Unfavorable.Cash decreases by the actual amount paid to direct laborers, which is Actual hours × Actual rate = 12,520 hours × $21.00 per hour = $262,920. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output, which is Standard hours × Standard rate = (12,800 units × 0.90 hours per unit) × $22.00 per hour = 11,520 hours × $22.00 per hour = $253,440. The difference consists of the Labor Rate Variance which is $12,520 Favorable and the Labor Efficiency Variance which is $22,000 Unfavorable.Cash decreases by the actual amount paid for various fixed overhead costs, which is $27,700. Work in Process increases by the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output multiplied by the predetermined overhead rate, which is (12,800 units × 0.90 hours per unit) × $6.50 per hour = 11,520 hours × $6.50 per hour = $74,880. Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) decreases by the amount of depreciation for the period, which is $105,000. The difference is the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Budget Variance which is $15,700 Unfavorable and the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Volume Variance which is $42,120 Unfavorable.Work in Process decreases by the number of units transferred to Finished Goods multiplied by the standard cost per unit = 12,800 units × $38.15 per unit = $488,320. Finished Goods increases by the same amount.Cash increases by the number of units sold multiplied by the selling price per unit, which is 12,600 units × $52.10 per unit = $656,460. Retained Earnings increases by the same amount.Finished Goods decreases by the number of units sold multiplied by their standard cost per unit, which is 12,600 units × $38.15 per unit = $480,690. Retained Earnings decreases by the same amount.Cash and Retained Earnings decrease by $73,000 to record the selling and administrative expenses.All variance accounts take their balance to zero and they are closed to Cost of Goods Sold (which resides within Retained Earnings).4.
The explanations for transactions a through i are as follows:Cash decreases by the actual cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Actual price = 36,300 pounds × $4.70 per pound = $170,610. Raw Materials increase by the standard cost of the raw materials purchased, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 36,300 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $181,500. The materials price variance is $10,890 Favorable.Raw Materials decrease by the standard cost of the raw materials used in production, which is Actual quantity × Standard price = 32,100 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $160,500. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard quantity of raw materials allowed for the actual output, which is Standard quantity × Standard price = (12,800 units × 2.5 pounds per unit) × $5.00 per pound = 32,000 pounds × $5.00 per pound = $160,000. The difference is the Materials Quantity Variance which is $500 Unfavorable.Cash decreases by the actual amount paid to direct laborers, which is Actual hours × Actual rate = 12,520 hours × $21.00 per hour = $262,920. Work in Process increases by the standard cost of the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output, which is Standard hours × Standard rate = (12,800 units × 0.90 hours per unit) × $22.00 per hour = 11,520 hours × $22.00 per hour = $253,440. The difference consists of the Labor Rate Variance which is $12,520 Favorable and the Labor Efficiency Variance which is $22,000 Unfavorable.Cash decreases by the actual amount paid for various fixed overhead costs, which is $27,700. Work in Process increases by the standard amount of hours allowed for the actual output multiplied by the predetermined overhead rate, which is (12,800 units × 0.90 hours per unit) × $6.50 per hour = 11,520 hours × $6.50 per hour = $74,880. Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) decreases by the amount of depreciation for the period, which is $105,000. The difference is the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Budget Variance which is $15,700 Unfavorable and the Fixed Overhead (FOH) Volume Variance which is $42,120 Unfavorable.Work in Process decreases by the number of units transferred to Finished Goods multiplied by the standard cost per unit = 12,800 units × $38.15 per unit = $488,320. Finished Goods increases by the same amount.Cash increases by the number of units sold multiplied by the selling price per unit, which is 12,600 units × $52.10 per unit = $656,460. Retained Earnings increases by the same amount.Finished Goods decreases by the number of units sold multiplied by their standard cost per unit, which is 12,600 units × $38.15 per unit = $480,690. Retained Earnings decreases by the same amount.Cash and Retained Earnings decrease by $73,000 to record the selling and administrative expenses.All variance accounts take their balance to zero and they are closed to Cost of Goods Sold (which resides within Retained Earnings).4.

Learning Objectives
- Understand the process of accurately logging transactions in a standard costing system.
- Develop the skill to determine the differences between actual expenditures and normative costs, including variations in direct materials, direct labor, and fixed overhead.
- Understand the process of preparing and analyzing income statements for manufacturing companies through standard costing techniques.