Asked by Orion Lavigne on Jul 03, 2024

Verified
The sampling distribution of 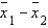 is normal if the sampled populations are normal, and approximately normal if the populations are nonnormal and the sample sizes
is normal if the sampled populations are normal, and approximately normal if the populations are nonnormal and the sample sizes 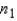 and
and 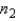 are large.
are large.
Sampling Distribution
The likelihood distribution of a specific statistic derived from a random selection.
Independent Sample
Samples that are collected in such a way that the selection of one sample does not influence the selection of another, ensuring that observations between samples are not related.
Normally Distributed
Describes a probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean.
- Evaluate the consequences of t-test analyses to infer about the means of populations.
- Master the underlying principles that justify the use of the t-test for two independent samples.

Verified Answer

Learning Objectives
- Evaluate the consequences of t-test analyses to infer about the means of populations.
- Master the underlying principles that justify the use of the t-test for two independent samples.
Related questions
The Pooled-Variances T-Test Requires That the Two Population Variances Need ...
In Testing the Difference Between Two Population Means Using Two ...
Automobile Insurance Appraisers Examine Cars That Have Been Involved in ...
The T-Test for the Difference Between the Means of Two ...
In Testing the Difference Between Two Population Means, Which of ...