Asked by Pedro Mendes da Fonseca on Apr 28, 2024

Verified
In testing the difference between two population means, which of the following assumptions is not true for the two-sample procedure that uses a pooled estimate of the common variance 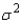 ?
?
A) The two samples must be independent of each other.
B) The two samples must be small and selected at random from the populations.
C) The populations from which the samples are drawn must be t-distributed.
D) The population variances should be equal or nearly equal.
E) None of these.
Pooled Estimate
A combined estimate derived from two or more sample estimates, often used in hypothesis testing or meta-analysis.
Two-Sample Procedure
A statistical method used to compare two independent samples to test a hypothesis about the difference between population parameters.
Common Variance
The shared variance between variables in a statistical model, often referring to the portion of variability that is accounted for by a common factor.
- Explain the circumstances in which the t-distribution can be utilized.
- Understand the assumptions underlying t-tests for independent samples.

Verified Answer

Learning Objectives
- Explain the circumstances in which the t-distribution can be utilized.
- Understand the assumptions underlying t-tests for independent samples.
Related questions
The T-Test for the Difference Between the Means of Two ...
Under What Conditions Can the T-Distribution Be Correctly Employed to ...
The T Test for Independent Samples Assumes Which of the ...
The Sampling Distribution of Is Normal If the Sampled ...
The Pooled-Variances T-Test Requires That the Two Population Variances Need ...