Asked by Tyson Fisher on Jul 27, 2024

Verified
The market demand and supply functions for alcohol at Major League Baseball games are: 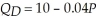 and
and 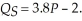 Calculate the equilibrium quantity and price and point elasticity of supply in equilibrium. Next, calculate producer surplus. Suppose that alcohol is taxed at $0.75 per unit at the games. Calculate the revenues generated by the tax. Calculate the loss in producer surplus. What percentage of the burden of the tax falls on producers?
Calculate the equilibrium quantity and price and point elasticity of supply in equilibrium. Next, calculate producer surplus. Suppose that alcohol is taxed at $0.75 per unit at the games. Calculate the revenues generated by the tax. Calculate the loss in producer surplus. What percentage of the burden of the tax falls on producers?
Point Elasticity
The measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in price at a specific point on the demand curve.
Producer Surplus
The difference between the amount a producer is paid for a good and the minimum amount they are willing to accept for producing it.
Equilibrium Quantity
The quantity of goods or services supplied is equal to the quantity demanded at the market price.
- Acquire insight into the notion of market equilibrium and the processes involved in its determination in different market scenarios.
- Ascertain the equilibrium point in terms of price and quantity across different commodities and services.
- Examine the effects of taxation on market balance, focusing on alterations in both consumer and producer surplus.

Verified Answer
ZK
Zybrea KnightJul 31, 2024
Final Answer :
First we must determine the market equilibrium quantity and price. To do this, we set quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied and solve for equilibrium price.QD = 10 - 0.04P = QS = 3.8P - 2
Therefore P = 3.13, and at this price the quantity exchanged will be 9.87. The point elasticity of supply is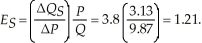 The producer surplus is:
The producer surplus is:
PS = 0.5(9.87)(3.13 - 0.53) = 12.83
If the market is taxed $0.75 per unit, the equilibrium price consumers pay is:
QD = 10 - 0.04 Pb = QS = 3.8(Pb - 0.75) - 2
Therefore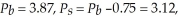 and the quantity exchanged is 9.85. The new level of producer surplus is:
and the quantity exchanged is 9.85. The new level of producer surplus is: 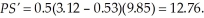 The change in producer surplus associated with the tax is -0.07. The tax generates tax revenues of $7.39. Producers bear
The change in producer surplus associated with the tax is -0.07. The tax generates tax revenues of $7.39. Producers bear 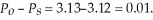 Consumers bear
Consumers bear 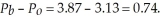 Producers bear 1.33 % of the tax.
Producers bear 1.33 % of the tax.
Therefore P = 3.13, and at this price the quantity exchanged will be 9.87. The point elasticity of supply is
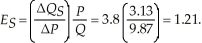 The producer surplus is:
The producer surplus is:PS = 0.5(9.87)(3.13 - 0.53) = 12.83
If the market is taxed $0.75 per unit, the equilibrium price consumers pay is:
QD = 10 - 0.04 Pb = QS = 3.8(Pb - 0.75) - 2
Therefore
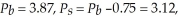 and the quantity exchanged is 9.85. The new level of producer surplus is:
and the quantity exchanged is 9.85. The new level of producer surplus is: 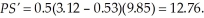 The change in producer surplus associated with the tax is -0.07. The tax generates tax revenues of $7.39. Producers bear
The change in producer surplus associated with the tax is -0.07. The tax generates tax revenues of $7.39. Producers bear 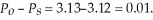 Consumers bear
Consumers bear 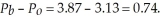 Producers bear 1.33 % of the tax.
Producers bear 1.33 % of the tax.
Learning Objectives
- Acquire insight into the notion of market equilibrium and the processes involved in its determination in different market scenarios.
- Ascertain the equilibrium point in terms of price and quantity across different commodities and services.
- Examine the effects of taxation on market balance, focusing on alterations in both consumer and producer surplus.