Asked by Josie Pagnucco on May 11, 2024

Verified
Sarah and Jane are two representative individuals living in an economy that produces two goods, X and Y. Sarah's and Jane's utility functions are given as:
Sarah: US = 100X0.5Y0.5
Jane: UJ = 50X0.4Y0.6
The market determined prices of X and Y are $10 and $20, respectively. Current outputs are 58 units of X per time period and 36 units of Y. Jane's current income is $600 per time period, while Sarah's income is $700 per time period.
a. Write expressions for Sarah and Jane's marginal rates of substitution.
b. Determine the quantities of X and Y that Sarah and Jane should consume in equilibrium.
c. Do the values calculated in part (b) satisfy the conditions for equilibrium in exchange? Explain using numbers.
d. Examine your answers in parts (b) and (c). If equilibrium has not been achieved, what would be necessary to reach equilibrium? If equilibrium has been achieved, comment on the process by which equilibrium was reached.
Marginal Rates
The amount of change in a variable (often related to costs or taxes) associated with a one-unit change in another variable.
Utility Functions
Mathematical representations describing the level of satisfaction or utility that a consumer derives from consuming a good or combination of goods.
Equilibrium
A state of balance in a market, where demand equals supply, and economic forces are at rest.
- Define and evaluate marginal rates of substitution within utility maximization challenges.
- Acquire knowledge of welfare economics principles, specifically the utility possibilities frontier, and how it showcases the efficient use of resources.
- Scrutinize trading situations between people to discover exchanges that provide mutual advantage.

Verified Answer
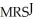 =
= 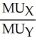 =
= 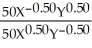 =
= 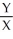 Sarah's MRS:
Sarah's MRS: 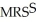 =
= 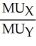 =
= 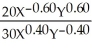 =
= 
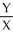 b.For equilibrium, each individual must equate MRS to
b.For equilibrium, each individual must equate MRS to 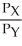 .
. 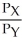 =
= 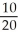 =
=  For Jane:
For Jane: 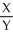 =
=  , Y =
, Y =  X
XFor Sarah:

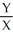 =
=  ,
, 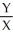 =
=  ∙
∙  Y =
Y =  X
XTo determine quantities substitute into each individuals budget constraint.
Jane's budget constraint: 600 = 10X + 20Y
Substitute Y = (1/2)X
600 = 10X + 20(1/2)X
600 = 10X + 10X
X = 30
600 = 10(30) + 20Y
300 = 20Y
Y = 15
Jane should consume 30 units of X and 15 units of Y.
Sarah's budget constraint: 700 = 10X + 20Y
Substitute Y = (3/4)X
700 = 10X + 20(3/4)X
700 = 25X
X = 28
700 = 10(28) + 20Y
420 = 20Y
Y = 21
Sarah should consume 28 units of X and 21 units of Y.
c.In equilibrium MRSJ should equal MRSS.
 =
= 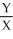 Jane is consuming 15 units of Y and 30 units of X.
Jane is consuming 15 units of Y and 30 units of X. 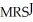 =
= 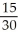 =
= 
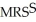 =
=  X
XSarah is consuming 21 units of Y and 28 units of X.
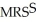 =
= 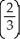
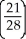 =
= 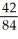 =
= 
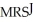 does equal
does equal 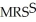 , and it is also True that the two individuals are consuming the available quantities of X and Y.
, and it is also True that the two individuals are consuming the available quantities of X and Y.d.Equilibrium has been achieved. The equilibrium involves an equilibrium in resource markets determining Jane's and Sarah's incomes, in the product market allocating L and K between X and Y, and the condition for efficiency in output that matches production to Jane and Sarah's preferences.

Learning Objectives
- Define and evaluate marginal rates of substitution within utility maximization challenges.
- Acquire knowledge of welfare economics principles, specifically the utility possibilities frontier, and how it showcases the efficient use of resources.
- Scrutinize trading situations between people to discover exchanges that provide mutual advantage.
Related questions
From a Point Within the Utilities Possibilities Frontier ...
What Is TRUE About Every Point Along a Utilities Possibilities ...
What Does the Negative Slope of the Utilities Possibilities Frontier ...
Which of the Following Is True at the Exchange Equilibrium ...
Two Individuals, a and B, Are Free to Engage in ...