Asked by Sameer Ishaq on May 12, 2024

Verified
Prejean Products, Incorporated, has a Relay Division that manufactures and sells a number of products, including a standard relay. Data concerning that relay appear below:
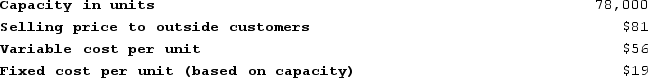 The company has a Electronics Division that could use this relay in one of its products. The Electronics Division is currently purchasing 9,000 of these relays per year from an overseas supplier at a cost of $74 per relay.
The company has a Electronics Division that could use this relay in one of its products. The Electronics Division is currently purchasing 9,000 of these relays per year from an overseas supplier at a cost of $74 per relay.
Required:
a. Assume that the Relay Division has enough idle capacity to handle all of the Electronics Division's needs. What is the acceptable range, if any, for the transfer price between the two divisions?
b. Assume that the Relay Division is selling all of the relays it can produce to outside customers. Also assume that $13 in variable expenses can be avoided on transfers within the company due to reduced shipping and selling costs. What is the acceptable range, if any, for the transfer price between the two divisions?
Transfer Price
The price at which goods and services are transferred between departments or units within the same organization.
Relay Division
A unit within a company dedicated to the production and sale of relay components or systems.
Electronics Division
A specialized branch within a company that focuses on the development, production, and sale of electronic goods and devices.
- Learn and illustrate the critical concepts of transfer pricing and the approved price ranges within a corporate framework.
- Inspect the consequences of capacity challenges on the operational decisions of production and pricing in a corporate context.
- Realize the importance of considering external supplier costs in transfer pricing decisions.

Verified Answer
Transfer price > Variable cost per unit + (Total contribution margin on lost sales ÷ Number of units transferred)
Transfer price > $56 per unit + ($0 ÷ 9,000 units) = $56 per unit + $0 per unit = $56 per unit
From the perspective of the purchasing division, the transfer is financially attractive if and only if:
Transfer price < Cost of buying from outside supplier
Transfer price < $74 per unit
Combining the two requirements, the range of acceptable transfer prices is:
$56 per unit < Transfer price < $74 per unit
b. The total contribution margin on lost sales is computed as follows:
 From the perspective of the selling division, profits would increase as a result of the transfer if and only if:
From the perspective of the selling division, profits would increase as a result of the transfer if and only if:Transfer price > Variable cost per unit + (Total contribution margin on lost sales ÷ Number of units transferred)
Transfer price > $43 per unit + ($225,000 ÷ 9,000 units) = $43 per unit + $25 per unit = $68 per unit
From the perspective of the purchasing division, the transfer is financially attractive if and only if:
Transfer price < Cost of buying from outside supplier
Transfer price < $74 per unit
Combining the two requirements, the range of acceptable transfer prices is: $68 per unit < Transfer price < $74 per unit

Learning Objectives
- Learn and illustrate the critical concepts of transfer pricing and the approved price ranges within a corporate framework.
- Inspect the consequences of capacity challenges on the operational decisions of production and pricing in a corporate context.
- Realize the importance of considering external supplier costs in transfer pricing decisions.
Related questions
Vandermeer Products, Incorporated, Has a Antennae Division That Manufactures and ...
Cominsky Products, Incorporated, Has a Screen Division That Manufactures and ...
Chesley Products, Incorporated, Has a Connector Division That Manufactures and ...
Liapis Products, Incorporated, Has a Valve Division That Manufactures and ...
Division Y Has Asked Division X of the Same Company ...