Asked by yasmine harper on Jun 24, 2024

Verified
Medical statistics show that deaths due to four major diseases - call them A, B, C and D - account for 15%, 21%, 18%, and 14%, respectively, of all non-accidental deaths. A study of the causes of 616 non-accidental deaths at a hospital give the following counts:  Do these data provide sufficient evidence to indicate that the proportions of people dying of diseases A, B, C, and D at this hospital differ from the proportions accumulated for the population at large?
Do these data provide sufficient evidence to indicate that the proportions of people dying of diseases A, B, C, and D at this hospital differ from the proportions accumulated for the population at large?
Find the approximate p-value and use it to make your decision.
Compute 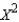 :
:
______________
Reject 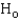 when
when 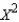 > ______________.
> ______________.
Thus the p-value ______________.
Conclude that the proportions of people dying of diseases A, B, C, and D at this hospital ______________ from the proportions for the larger population.
Non-accidental Deaths
Refers to deaths resulting from causes other than accidents, such as diseases or intentional harm.
P-value
The chance of getting test outcomes that are as significant or more so than what was actually seen, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
Major Diseases
Serious or significant health conditions that impact a large portion of a population or have substantial effects on individuals’ health and quality of life.
- Gain familiarity with the techniques for implementing chi-square goodness-of-fit investigations.
- Assess the conclusions of statistical examinations to guide decision processes.
- Distinguish among various data types and suitable statistical analyses.

Verified Answer

Learning Objectives
- Gain familiarity with the techniques for implementing chi-square goodness-of-fit investigations.
- Assess the conclusions of statistical examinations to guide decision processes.
- Distinguish among various data types and suitable statistical analyses.
Related questions
The Four Most Popular Flavors of a Particular Brand of ...
In a Goodness-Of-Fit Test,the Null Hypothesis States That the Data ...
In a Goodness-Of-Fit Test,the Null Hypothesis States That the Data ...
Which of the Following Statements About the Spearman Rank-Correlation Coefficient ...
You Can Only Conduct Two-Tail Tests of the Spearman Rank ...