Asked by Aamir Anwar on May 07, 2024

Verified
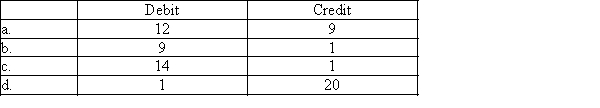
Listed below are accounts to use for transactions (a) through (d), each identified by a number. Following this list are the transactions. You are to indicate for each transaction the accounts that should be debited and credited by placing the account number(s) in the appropriate box.
1.Cash
2.Accounts Receivable
3.Office Supplies
4.Land
5.Interest Receivable
6.Building
7.Truck
8.Equipment
9.Accounts Payable
10.Interest Payable
11.Insurance Payable
12.Utilities Expense
13.Notes Payable
14.Prepaid Insurance
15.Service Revenue
16.Common Stock
17.Insurance Expense
18.Interest Expense
19.Office Supplies Expense
20.Unearned Service Revenue
21.Dividends 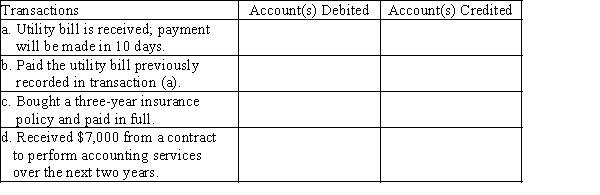
Interest Receivable
An accounting term referring to the interest income that has been earned but not yet received in cash.
Accounts Payable
Liabilities of a business that represent amounts due to suppliers or creditors for goods and services received but not yet paid for.
Equipment
Tangible assets used in the operation of a business, such as machinery and office furniture, which are not intended for sale.
- Perform journal entries for various business transactions, applying the double-entry bookkeeping system.

Verified Answer

Learning Objectives
- Perform journal entries for various business transactions, applying the double-entry bookkeeping system.
Related questions
On January 12, JumpStart Co ...
On January 1, Merry Walker and Other Stockholders Established a ...
Which of the Following Describes the Transaction Resulting in a ...
Information May Be Accessed Almost Instantly and Made Available to ...
Formatted Screens and Built-In Databases of Patient Accounts and Vendors ...