Asked by Tyesha Valles on Jul 22, 2024

Verified
Laraia Corporation has provided the following contribution format income statement.All questions concern situations that are within the relevant range. 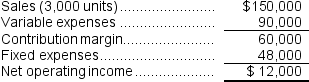 Required:
Required:
a.What is the contribution margin per unit?
b.What is the contribution margin ratio?
c.What is the variable expense ratio?
d.If sales increase to 3,050 units, what would be the estimated increase in net operating income?
e.If sales decline to 2,900 units, what would be the estimated net operating income?
f.If the selling price increases by $4 per unit and the sales volume decreases by 200 units, what would be the estimated net operating income?
g.If the variable cost per unit increases by $5, spending on advertising increases by $3,000, and unit sales increase by 450 units, what would be the estimated net operating income?
h.What is the break-even point in unit sales?
i.What is the break-even point in dollar sales?
j.Estimate how many units must be sold to achieve a target profit of $54,000.
k.What is the margin of safety in dollars?
l.What is the margin of safety percentage?
m.What is the degree of operating leverage?
n.Using the degree of operating leverage, what is the estimated percent increase in net operating income of a 15% increase in sales?
Contribution Margin
The amount remaining from sales revenue after variable costs have been deducted, indicating how much contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit.
Variable Expense Ratio
A financial metric that measures variable costs as a percentage of sales, reflecting how those costs fluctuate with production output.
Operating Leverage
A measure of how sensitive a company's operating income is to a change in sales volume, indicating the level of fixed costs in the business structure.
- Assemble and investigate contribution format income statements in varying conditions.
- Acquire knowledge on the concept of break-even point calculation in both units and dollars.
- Compute and examine the effects of variations in variable costs, fixed costs, and selling prices on an organization's financial outcomes.

Verified Answer
JC
Jennell CrespoJul 22, 2024
Final Answer :
a. 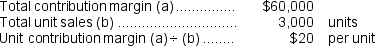 Alternatively,
Alternatively, 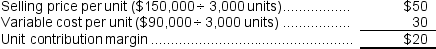 b.CM ratio = Contribution margin ÷ Sales = $60,000 ÷ $150,000 = 40%
b.CM ratio = Contribution margin ÷ Sales = $60,000 ÷ $150,000 = 40%
c.Variable expense ratio = Variable expenses ÷ Sales = $90,000 ÷ $150,000 = 60%
d.The increase in net operating income would be the increased contribution margin because fixed expenses are not affected.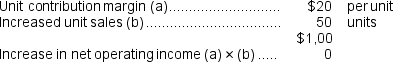 e.
e.  f.
f. 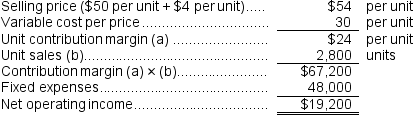 g.
g. 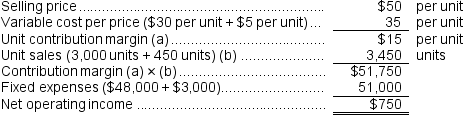 h.Unit sales to break even = Fixed expenses ÷ Unit CM = $48,000 ÷ $20 per unit = 2,400 units
h.Unit sales to break even = Fixed expenses ÷ Unit CM = $48,000 ÷ $20 per unit = 2,400 units
i.Dollar sales to break even = Fixed expenses ÷ CM ratio = $48,000 ÷ 40% = $120,000
j.Unit sales to attain a target profit = (Target profit + Fixed expenses)÷ Unit CM
= ($54,000 + $48,000)÷ $20 per unit = $102,000÷ $20 per unit = 5,100 units
k.Margin of safety in dollars = Total budgeted (or actual)sales - Break-even sales
= $150,000 − $120,000 = $30,000
l.Margin of safety percentage = Margin of safety in dollars ÷ Total budgeted (or actual)sales
= $30,000 ÷ $150,000 = 20%
m.Degree of operating leverage = Contribution margin ÷ Net operating income
= $60,000 ÷ $12,000 = 5.0
n.Percentage change in net operating income = Degree of operating leverage × Percentage change in sales
= 5.0 × 15% = 75%
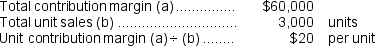 Alternatively,
Alternatively, 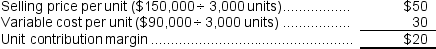 b.CM ratio = Contribution margin ÷ Sales = $60,000 ÷ $150,000 = 40%
b.CM ratio = Contribution margin ÷ Sales = $60,000 ÷ $150,000 = 40%c.Variable expense ratio = Variable expenses ÷ Sales = $90,000 ÷ $150,000 = 60%
d.The increase in net operating income would be the increased contribution margin because fixed expenses are not affected.
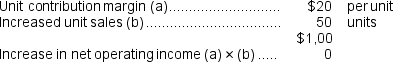 e.
e.  f.
f. 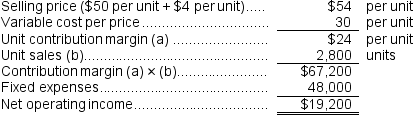 g.
g. 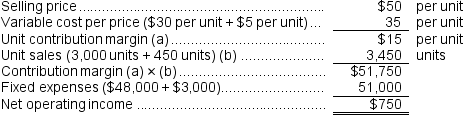 h.Unit sales to break even = Fixed expenses ÷ Unit CM = $48,000 ÷ $20 per unit = 2,400 units
h.Unit sales to break even = Fixed expenses ÷ Unit CM = $48,000 ÷ $20 per unit = 2,400 unitsi.Dollar sales to break even = Fixed expenses ÷ CM ratio = $48,000 ÷ 40% = $120,000
j.Unit sales to attain a target profit = (Target profit + Fixed expenses)÷ Unit CM
= ($54,000 + $48,000)÷ $20 per unit = $102,000÷ $20 per unit = 5,100 units
k.Margin of safety in dollars = Total budgeted (or actual)sales - Break-even sales
= $150,000 − $120,000 = $30,000
l.Margin of safety percentage = Margin of safety in dollars ÷ Total budgeted (or actual)sales
= $30,000 ÷ $150,000 = 20%
m.Degree of operating leverage = Contribution margin ÷ Net operating income
= $60,000 ÷ $12,000 = 5.0
n.Percentage change in net operating income = Degree of operating leverage × Percentage change in sales
= 5.0 × 15% = 75%

Learning Objectives
- Assemble and investigate contribution format income statements in varying conditions.
- Acquire knowledge on the concept of break-even point calculation in both units and dollars.
- Compute and examine the effects of variations in variable costs, fixed costs, and selling prices on an organization's financial outcomes.