Asked by Egypt Falaah on Jun 24, 2024

Verified
Flyer Corporation manufactures two products, Product A and Product B.Product B is of fairly recent origin, having been developed as an attempt to enter a market closely related to that of Product A.Product B is the more complex of the two products, requiring three hours of direct labor time per unit to manufacture compared to one and one-half hours of direct labor time for Product A.Product B is produced on an automated production line.
Overhead is currently assigned to the products on the basis of direct-labor-hours.The company estimated it would incur $396,000 in manufacturing overhead costs and produce 5,500 units of Product B and 22,000 units of Product A during the current year.Unit costs for materials and direct labor are: 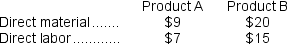 Required:
Required:
a.Compute the predetermined overhead rate under the current method of allocation and determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.
b.The company's overhead costs can be attributed to four major activities.These activities and the amount of overhead cost attributable to each for the current year are given below: 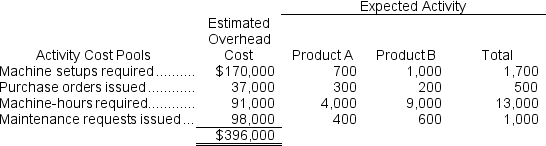 Using the data above and an activity-based costing approach, determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.
Using the data above and an activity-based costing approach, determine the unit product cost of each product for the current year.
Direct-Labor-Hours
The total hours worked by employees that are directly involved in the manufacturing process.
Predetermined Overhead Rate
A rate used to apply manufacturing overhead costs to products, calculated before the production period begins based on estimated costs and activity levels.
Automated Production Line
A manufacturing process involving the use of robotics and computer-controlled equipment to perform a sequence of operations automatically.
- Identify and compare the key features of traditional costing and activity-based costing models.
- Evaluate the unit cost of products by applying the standard costing methodology.
- Estimate the product unit costs by implementing the activity-based costing (ABC) method.

Verified Answer
 Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:
Using these hours as a base, the predetermined overhead using direct labor-hours would be:Predetermined overhead rate = Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost ÷ Estimated total amount of the allocation base = $396,000 ÷ 49,500 DLHs = $8.00 per DLH
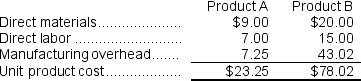
Using this overhead rate, the unit product cost of each product would be:
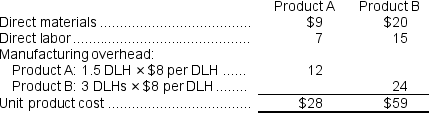 b.The overhead rates are computed as follows:
b.The overhead rates are computed as follows: 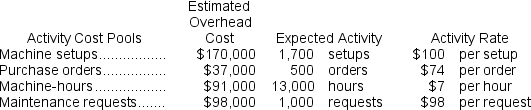 The overhead cost charged to each product is:
The overhead cost charged to each product is:The overhead cost charged to Product A is:
 Overhead cost per unit of Product A = $159,400 ÷ 22,000 units = $7.25 per unit (rounded)
Overhead cost per unit of Product A = $159,400 ÷ 22,000 units = $7.25 per unit (rounded)The overhead cost charged to Product B is:
 Overhead cost per unit of Product B = $236,600 ÷ 5,500 units = $43.02 per unit (rounded)
Overhead cost per unit of Product B = $236,600 ÷ 5,500 units = $43.02 per unit (rounded)Using activity-based costing, the unit product cost of each product would be:

Learning Objectives
- Identify and compare the key features of traditional costing and activity-based costing models.
- Evaluate the unit cost of products by applying the standard costing methodology.
- Estimate the product unit costs by implementing the activity-based costing (ABC) method.
Related questions
Thingvold, Inc ...
Departmental Overhead Rates Applied on the Basis of a Volume ...
In Activity-Based Costing, a Plantwide Overhead Rate Is Used to ...
What Are Three Advantages of Activity-Based Costing Over Traditional Volume-Based ...
Activity-Based Costing Is a Method of Accumulating and Allocating Costs ...