Asked by Jaleel Joshua on Jul 14, 2024

Verified
Duane breeds parrots for a living. He has discovered that the production function for parrot chicks (Q) is:
Q = K1/2L1/2
where K is capital (for example nest boxes, cages and the like) and L is parrot food. The marginal products of capital and labor are as follows:
MPK = .5K-1/2L1/2 MPL = .5K1/2L-1/2
The price of K is $8 and the price of L is $2.
a. What type of production function is this?
b. Does this production function exhibit constant, increasing or decreasing returns to scale? Explain.
c. What is the average product of capital?
d. Does capital obey the "law of diminishing returns?" Explain.
e. Suppose that Duane wants 144 parrot chicks, how much K and L should be employed to minimize costs, and what is the cost of producing 144 parrot chicks?
f. Suppose that Duane is faced with the same problem as in (f) except that he has a fixed amount of K. In fact, K = 16. How much L should be employed to minimize costs, and what is the total cost?
Production Function
A mathematical model describing the relation between input quantities and their respective outputs.
Marginal Products
A new definition for the additional units of output gained by employing one more unit of a specific input, keeping all other inputs constant.
Law of Diminishing Returns
An economic principle stating that as investment in a particular area increases, the rate of profit from that investment, after a certain point, cannot continue to increase if other inputs remain the same.
- Interpret the implications of production function properties, such as returns to scale and the law of diminishing returns, on operational decisions.
- Formulate strategies for cost minimization in production through optimal allocation of resources.

Verified Answer
KH
Kameron HatcherJul 19, 2024
Final Answer :
a.Cobb-Douglas.
b.This production function exhibits constant returns to scale because σ + β = 1.
c.APK =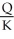 =
= 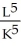 d.Yes, capital obeys "the law of diminishing returns" because as K increases, MPK decreases (K is in the denominator).
d.Yes, capital obeys "the law of diminishing returns" because as K increases, MPK decreases (K is in the denominator).
e.This problem is solved using the method of Lagrange multipliers. The Lagrangian is:
Φ = 8K + 2L + λ(K.5L.5 - 144)
Differentiating with respect to K, L and λ yields:
∂Φ/∂K = 8 + λ(.5L.5/K.5)
∂Φ/∂L = 2 + λ(.5K.5/L.5)
∂Φ/∂λ = K.5L.5 - 144
Setting these derivatives equal to zero and solving for K, L and λ yields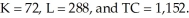 f.If K = 16, then Q = 4L.5.
f.If K = 16, then Q = 4L.5.
Thus, for Q = 144, L = 1,296 and TC = 2,720.
b.This production function exhibits constant returns to scale because σ + β = 1.
c.APK =
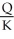 =
= 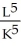 d.Yes, capital obeys "the law of diminishing returns" because as K increases, MPK decreases (K is in the denominator).
d.Yes, capital obeys "the law of diminishing returns" because as K increases, MPK decreases (K is in the denominator).e.This problem is solved using the method of Lagrange multipliers. The Lagrangian is:
Φ = 8K + 2L + λ(K.5L.5 - 144)
Differentiating with respect to K, L and λ yields:
∂Φ/∂K = 8 + λ(.5L.5/K.5)
∂Φ/∂L = 2 + λ(.5K.5/L.5)
∂Φ/∂λ = K.5L.5 - 144
Setting these derivatives equal to zero and solving for K, L and λ yields
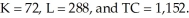 f.If K = 16, then Q = 4L.5.
f.If K = 16, then Q = 4L.5.Thus, for Q = 144, L = 1,296 and TC = 2,720.

Learning Objectives
- Interpret the implications of production function properties, such as returns to scale and the law of diminishing returns, on operational decisions.
- Formulate strategies for cost minimization in production through optimal allocation of resources.