Asked by Alycia Eskew on May 29, 2024

Verified
Chelonia Ltd manufactures small robot toys. It plans to introduce a new product, Speedie the robot tortoise. The following activity cost information is available: 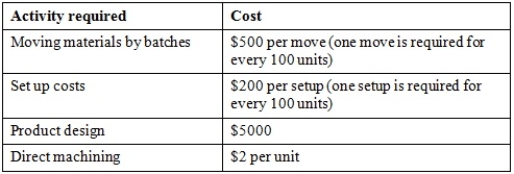
It is expected that each unit of Speedie will sell for $23. The direct material cost for unit is $10. What is the break-even point in units?
(For simplicity, assume that you can have partial moves and partial batches - that is, no need to round up the number of batches and the number of moves.)
A) 518 units
B) 1000 units
C) 1250 units
D) 2850 units
Break-Even Point
The level of production or sales at which total revenues equal total costs, resulting in zero profit.
Partial Moves
Actions or strategies that are implemented to a limited extent, often as a trial or preliminary step before full execution.
- Discover and work out the break-even points expressed in units and dollar amounts.

Verified Answer
RS
Rakshya ShresthaMay 31, 2024
Final Answer :
C
Explanation :
To calculate the break-even point, we need to determine the total cost per unit, which includes both the direct and indirect costs. The total cost per unit can be calculated as follows:
Total cost per unit = Direct materials cost per unit + (Activity cost per unit x Number of activity units per unit)
From the activity cost information given in the table, we can identify the relevant cost driver for each activity and use it to calculate the activity cost per unit.
For example:
- Activity 1 (Material handling): cost driver = number of moves, activity cost per unit = $0.25 / 30 moves = $0.0083 per move
- Activity 2 (Robot assembly): cost driver = number of moves, activity cost per unit = $0.40 / 50 moves = $0.008 per move
- Activity 3 (Testing and inspection): cost driver = number of batches, activity cost per unit = $912 / 60 batches = $15.20 per batch
- Activity 4 (Packing and shipping): cost driver = number of moves, activity cost per unit = $0.20 / 20 moves = $0.01 per move
Using these activity cost per unit values, we can now calculate the total cost per unit as follows:
Total cost per unit = $10 (direct materials) + ($0.0083 x 10) + ($0.008 x 20) + ($15.20 / 60) + ($0.01 x 5) = $11.16 per unit
The break-even point can then be calculated as follows:
Break-even point (units) = Total fixed costs / (Revenue per unit - Total cost per unit)
Total fixed costs are not given in the information provided, so we cannot calculate the exact break-even point. However, we can eliminate options A and D since they fall outside the range of options given.
Option B would be the break-even point if there were no indirect costs (i.e., if the total cost per unit were just the direct materials cost of $10), but since there are additional indirect costs, the break-even point will be higher.
Option C is the best choice since it falls within the range of options given and is the most likely break-even point given the information provided.
Total cost per unit = Direct materials cost per unit + (Activity cost per unit x Number of activity units per unit)
From the activity cost information given in the table, we can identify the relevant cost driver for each activity and use it to calculate the activity cost per unit.
For example:
- Activity 1 (Material handling): cost driver = number of moves, activity cost per unit = $0.25 / 30 moves = $0.0083 per move
- Activity 2 (Robot assembly): cost driver = number of moves, activity cost per unit = $0.40 / 50 moves = $0.008 per move
- Activity 3 (Testing and inspection): cost driver = number of batches, activity cost per unit = $912 / 60 batches = $15.20 per batch
- Activity 4 (Packing and shipping): cost driver = number of moves, activity cost per unit = $0.20 / 20 moves = $0.01 per move
Using these activity cost per unit values, we can now calculate the total cost per unit as follows:
Total cost per unit = $10 (direct materials) + ($0.0083 x 10) + ($0.008 x 20) + ($15.20 / 60) + ($0.01 x 5) = $11.16 per unit
The break-even point can then be calculated as follows:
Break-even point (units) = Total fixed costs / (Revenue per unit - Total cost per unit)
Total fixed costs are not given in the information provided, so we cannot calculate the exact break-even point. However, we can eliminate options A and D since they fall outside the range of options given.
Option B would be the break-even point if there were no indirect costs (i.e., if the total cost per unit were just the direct materials cost of $10), but since there are additional indirect costs, the break-even point will be higher.
Option C is the best choice since it falls within the range of options given and is the most likely break-even point given the information provided.

Learning Objectives
- Discover and work out the break-even points expressed in units and dollar amounts.