Asked by Duval Demps on May 29, 2024

Verified
Calculate the price of a call option using the Black Scholes model and the following data: stock price = $47.30, exercise price = $50, time to expiration = 85 days, risk-free rate = 3%, standard deviation = 35%.
A) $1.11
B) $2.22
C) $3.33
D) $4.44
Black Scholes Model
A mathematical model used for pricing European call and put options, evaluating the options' theoretical value based on several factors including time, price, volatility, and the risk-free interest rate.
Exercise Price
The price at which the holder of an option can buy (for a call option) or sell (for a put option) the underlying asset.
Standard Deviation
A measure of the dispersion or variation in a set of values, indicating how much the numbers in the set deviate from the mean (average).
- Learn about the Black-Scholes model and its role in computing the prices of options.

Verified Answer
d1 =
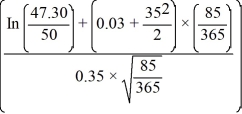 = -0.2029
= -0.2029d2 = -0.2029 - 0.35 ×
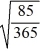 = -0.3718
= -0.3718N(d1) = 0.4196
N(d2) = 0.3550
Call value = S0N(d1) - Xe-rTN(d2) = (47.30) × (0.4196) - (50) × e-(0.03)(0.233) × 0.3550 = $2.22

Learning Objectives
- Learn about the Black-Scholes model and its role in computing the prices of options.
Related questions
You Calculate the Black-Scholes Value of a Call Option as ...
In Order for a Binomial Option Price to Approach the ...
The Current Stock Price of KMW Is $27, the Risk-Free ...
Which of the Inputs in the Black-Scholes Option Pricing Model ...
According to the Black-Scholes Model, When the Exercise Price Is ...