Asked by Cydney Adger on Jun 17, 2024

Verified
Buzby Corporation manufactures numerous products, one of which is called Epsilon-39. The company has provided the following data about this product:
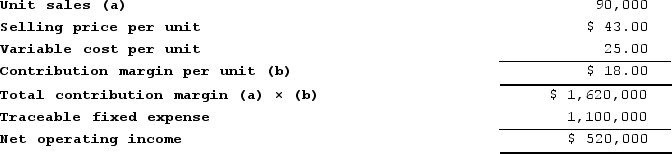 Required:a. Management is considering decreasing the price of Epsilon-39 by 5%, from $43.00 to $40.85. The company's marketing managers estimate that this price reduction would increase unit sales by 10%, from 90,000 units to 99,000 units. Assuming that the total traceable fixed expense does not change, what net operating income will Epsilon-39 earn at a price of $40.85 if this sales forecast is correct?b. Assuming that the total traceable fixed expense does not change, how many units of Epsilon-39 would Buzby need to sell at a price of $40.85 to earn the same net operating income that it currently earns at a price of $43.00? (Round your answer up to the nearest whole number.)
Required:a. Management is considering decreasing the price of Epsilon-39 by 5%, from $43.00 to $40.85. The company's marketing managers estimate that this price reduction would increase unit sales by 10%, from 90,000 units to 99,000 units. Assuming that the total traceable fixed expense does not change, what net operating income will Epsilon-39 earn at a price of $40.85 if this sales forecast is correct?b. Assuming that the total traceable fixed expense does not change, how many units of Epsilon-39 would Buzby need to sell at a price of $40.85 to earn the same net operating income that it currently earns at a price of $43.00? (Round your answer up to the nearest whole number.)
Traceable Fixed Expense
Fixed expenses specifically attributable to a particular section of a business or an operation.
Price Reduction
A strategy involving the lowering of the selling price of products or services, typically to attract more customers or respond to market competition.
- Gain insight into the computation of net operating income and its relevance to strategic business decisions.
- Gain insight into the procedures for break-even and profitability analysis under a range of pricing and cost circumstances.

Verified Answer
SP
Sankalp PatelJun 23, 2024
Final Answer :
a.The profit at the price of ${{[a(9)]:#,##0.00}} per unit is computed as follows:Profit = (Selling price per unit − Variable cost per unit) × Quantity sold − Fixed expensesProfit = (${{[a(9)]:#,##0.00}} per unit − ${{[a(3)]:#,##0.00}} per unit) × {{[a(11)]:#,###}} units − ${{[a(6)]:#,###}}Profit = (${{[a(12)]:#,##0.00}} per unit) × {{[a(11)]:#,###}} units − ${{[a(6)]:#,###}}Profit = ${{[a(13)]:#,###}} − ${{[a(6)]:#,###}} = ${{[a(14)]:#,###}}b.Profit = (Selling price per unit − Variable cost per unit) × Quantity sold − Fixed expenses${{[a(7)]:#,###}} = (${{[a(9)]:#,##0.00}} per unit − ${{[a(3)]:#,##0.00}} per unit) × Quantity sold − ${{[a(6)]:#,###}}${{[a(5)]:#,###}} = (${{[a(9)]:#,##0.00}} per unit − ${{[a(3)]:#,##0.00}} per unit) × Quantity sold${{[a(5)]:#,###}} = (${{[a(12)]:#,##0.00}} per unit) × Quantity sold Quantity sold = ${{[a(5)]:#,###}} ÷ ${{[a(12)]:#,##0.00}} per unit = {{[a(15)]:#,###}} units (rounded up)

Learning Objectives
- Gain insight into the computation of net operating income and its relevance to strategic business decisions.
- Gain insight into the procedures for break-even and profitability analysis under a range of pricing and cost circumstances.
Related questions
Algood Corporation Manufactures Numerous Products, One of Which Is Called ...
The Net Operating Income in the Flexible Budget for January ...
Net Operating Income Is Income Before Interest and Taxes
In Service Department Cost Allocations, Sales Dollars Should Be Used ...
For Performance Evaluation Purposes, the Actual Fixed Costs of a ...