Asked by Mariya&Eliza George on Jun 23, 2024

Verified
A dog kennel manager was interested in determining whether there is a difference in the time it takes a dog to complete an obstacle course for two different courses. A random sample of 36 dogs was selected and the time it took each dog to complete each course was recorded. In twelve cases it took the dog longer to complete course #1. Use the normal approximation to the sign test to determine if there is a significant difference in the time it takes to complete the two obstacle courses. Use 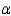 = 0.05.
= 0.05.
The null and alternate hypotheses are: 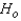 : The distributions of completion time for an obstacle course are identical for the two different courses, and p = 0.50.
: The distributions of completion time for an obstacle course are identical for the two different courses, and p = 0.50. 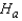 : The distributions of completion time for an obstacle course are not identical for the two different courses, and p
: The distributions of completion time for an obstacle course are not identical for the two different courses, and p  0.50.
0.50.
What is the z-statistic?
______________
What is the critical value for the test statistic?
Reject 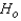 if |z| > ______________
if |z| > ______________
______________
Conclude that the distributions of completion time for an obstacle course are ______________ for the two different courses.
Normal Approximation
A method used to estimate the shape of a binomial distribution using a normal distribution when the sample size is large.
Sign Test
A non-parametric test used to determine if there is a statistically significant difference between paired or matched samples by examining the signs of differences without assuming any particular distribution.
Obstacle Courses
Physical or metaphorical challenges composed of multiple obstacles that require agility, strength, and strategic thinking to navigate or overcome.
- Acquire knowledge on the methodology and interpretation involved in the sign test for the comparison of two related samples.
- Comprehend the foundational conditions and assumptions behind diverse significance testing methodologies, specifically including experiments on paired differences.

Verified Answer

Learning Objectives
- Acquire knowledge on the methodology and interpretation involved in the sign test for the comparison of two related samples.
- Comprehend the foundational conditions and assumptions behind diverse significance testing methodologies, specifically including experiments on paired differences.
Related questions
A Paired-Difference Experiment Was Conducted to Compare Two Populations ...
Twenty Students Are Given an Attitude Test Before and After ...
A Car Dealer Was Interested in Comparing Two Brands of ...
The Principal of a High School Randomly Selected 30 Students ...
A Quality Control Manager at a Bottling Plant Wishes to ...