Asked by Emily Gutierrez on Jun 09, 2024

Verified
Whiston Corporation uses the weighted-average method in its process costing system. The following data were taken from the records of the first processing department for a recent month.
 Required:a. How many units were transferred to the next department during the month?b. What were the equivalent units of production for materials and for conversion costs for the month?c. What were the costs per equivalent unit of production for materials and for conversion costs for the month?d. What was the cost of the ending work in process inventory in the department at the end of the month?e. What was the cost of the units completed and transferred to the next department during the month?
Required:a. How many units were transferred to the next department during the month?b. What were the equivalent units of production for materials and for conversion costs for the month?c. What were the costs per equivalent unit of production for materials and for conversion costs for the month?d. What was the cost of the ending work in process inventory in the department at the end of the month?e. What was the cost of the units completed and transferred to the next department during the month?
Weighted-Average Method
A method in cost accounting used to average costs and quantities over a specific period, often applied in inventory valuation and costing of goods sold.
Process Costing
A costing system used where identical or similar products are mass-produced, allocating costs over the units produced during a period.
Conversion Costs
The combined costs of direct labor and manufacturing overhead incurred to transform raw materials into finished goods.
- Gauge equivalent units of production in accordance with the weighted-average method.
- Compute the cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion costs.

Verified Answer
b. Weighted-average method equivalent units of production
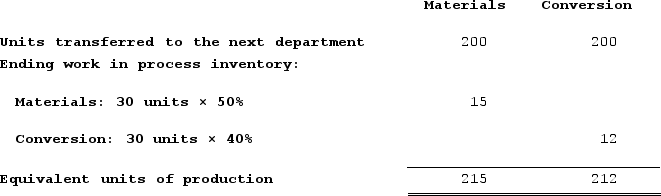 c. Weighted-average method cost per equivalent unit
c. Weighted-average method cost per equivalent unit d. Weighted-average method:
d. Weighted-average method: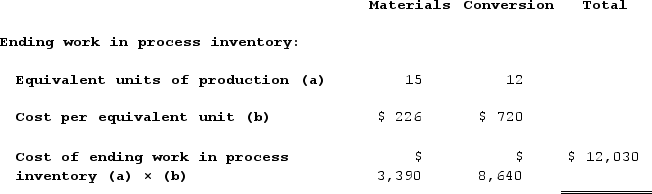 e. Weighted-average method:
e. Weighted-average method: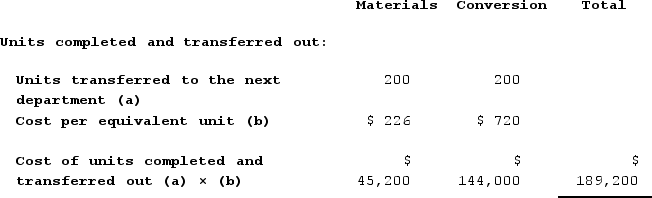

Learning Objectives
- Gauge equivalent units of production in accordance with the weighted-average method.
- Compute the cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion costs.
Related questions
Greenham Corporation Uses the Weighted-Average Method in Its Process Costing ...
Sharp Corporation Has a Process Costing System ...
Holling Incorporated Uses the Weighted-Average Method in Its Process Costing ...
Bachelet Incorporated Uses the Weighted-Average Method in Its Process Costing ...
Mccabe Corporation Uses the Weighted-Average Method in Its Process Costing ...