Asked by Bijeta Pradhan on Jul 08, 2024

Verified
When the necessary conditions are met, a two-tailed test is being conducted to test the difference between two population proportions. The two sample proportions are 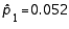 and
and 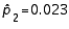 , and the standard error of the sampling distribution of
, and the standard error of the sampling distribution of 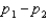 is 0.0085. The calculated value of the test statistic will be z = 3.41.
is 0.0085. The calculated value of the test statistic will be z = 3.41.
Two-Tailed Test
A statistical test of hypothesis where the area of interest spans both tails of the distribution, allowing for investigation of deviations in two opposite directions.
Sample Proportions
The fraction or percentage of observations in a sample that fall into one particular category or class.
Standard Error
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic, commonly the mean, indicating the variation of a sample statistic from the population parameter.
- Derive the test statistic for contrasting proportions between two populations.

Verified Answer

Learning Objectives
- Derive the test statistic for contrasting proportions between two populations.
Related questions
A Manufacturing Plant Has Two Assembly Lines for Producing Plastic ...
Use the Given Sample Data to Test the Claim That \(\text ...
A Cable Company in Michigan Is Thinking of Offering Its ...
When the Necessary Conditions Are Met, a Two-Tailed Test Is ...
The Environmental Protection Agency Wanted to Compare the Proportion of ...