Asked by Ikhlas Salih on Jul 02, 2024
Two independent random samples of sizes  and
and 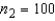 have been selected from binomial populations with parameters
have been selected from binomial populations with parameters 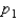 and
and 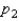 , respectively, and resulted in 38 and 65 success, respectively. Then the standard error of
, respectively, and resulted in 38 and 65 success, respectively. Then the standard error of 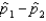 is estimated as .077.
is estimated as .077.
Binomial Populations
Groups of individuals or events subjected to a binomial experiment, where outcomes are categorized into two distinct categories.
Independent Random Samples
Groups of randomly selected samples from a population where the selection of an item for one sample does not influence the selection for another sample.
Standard Error
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic, most commonly the mean, which provides a measure of its precision.
- Comprehend and utilize the notion of standard error within the framework of confidence intervals.

Learning Objectives
- Comprehend and utilize the notion of standard error within the framework of confidence intervals.