Asked by Allison Belew on Jul 07, 2024

Verified
The random variable x is defined as the number of mistakes made by a typist on a randomly chosen page of a physics thesis. The probability distribution follows.
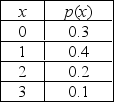 Round your answer to four decimal places, if necessary.
Round your answer to four decimal places, if necessary.
a. What is E(x)?
______________
b. Find
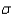 .
.
______________
c. Find P(x < 1).
______________
d. Find
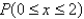 .
.
______________
e. In what fraction of pages in the thesis would the number of mistakes made be within two standard deviations of the mean?
______________
Probability Distribution
A function in mathematics that calculates the chances of various outcomes happening in an experiment.
E(x)
The expected value of a random variable, representing the mean or average value the variable takes over a large number of experiments or trials.
- Compute the average (expected value) and standard deviation for a specified probability distribution.
- Comprehend and compute probabilities linked to discrete random variables.

Verified Answer
JN

Learning Objectives
- Compute the average (expected value) and standard deviation for a specified probability distribution.
- Comprehend and compute probabilities linked to discrete random variables.
Related questions
{Blackjack Narrative} Find the Following Probabilities ...
The Number X of People Entering the Intensive Care Unit ...
{Retries Narrative} What Is the Variance for the Number of ...
Confirmed Cases of West Nile Virus in Birds for a ...
For a Discrete Random Variable A,the Probability Distribution of the ...