Asked by Mandalyns Watters on May 01, 2024

Verified
The market for paper in a particular region has the supply and demand curves:
QD = 160,000 - 2,000P QS = 40,000 + 2,000P,
where Q is measured in hundred-pound lots, and P is price per hundred-pound lot. There is currently no attempt to regulate the dumping of effluent into streams and rivers by the paper mills. As a result, dumping is widespread. The marginal external cost associated with the paper production is given by the expression:
MEC = 0.0002Q.
a. Calculate the competitive price and output, assuming that no attempt is made to monitor or regulate the dumping of effluent.
b. Determine the socially optimal levels for price and output. If your answers in (a) and (b) are different, explain the source of the difference.
c. Sketch a diagram showing the costs or benefits to society of allowing the market to operate in an unregulated fashion.
Marginal External Cost
The additional cost incurred by society as a whole due to one more unit of a good being produced, not accounted for by the producer.
Competitive Price
The price at which a product or service is sold that is reasonably close to the prices of competing products or services in the same market.
Socially Optimal Levels
Situations or outcomes in an economy that are considered the best from the standpoint of society as a whole, often involving efficient allocation of resources.
- Recognize the influence of externalities on the effectiveness of markets and the optimal societal production and consumption rates.
- Recognize the principles of marginal private cost, marginal external cost, and marginal social cost.
- Compute the optimal level of production taking into account external costs.

Verified Answer
MM
Marissa MorfordMay 06, 2024
Final Answer :
a.Solve for P in the demand and supply equations
P = 80 - 0.0005QD
P = 20 + 0.0005QS
Equate demand and supply
80 - 0.0005Q = 20 + 0.0005Q
60 = 0.001Q
Q = 60,000
P = 20 + 0.0005(60,000)
P = 20 + 30
P = 50
b.Socially optimal level is where demand intersects MSC
MSC = MC + MEC
MC is equal to supply
MSC = (20 + 0.0005Q) + 0.0002Q
MSC = 20 + 0.0007Q
Equate demand to MSC
80 - 0.0005Q = 20 + 0.0007Q
60 = 0.0012Q
Q = 50,000
P = 20 + 0.0005(50,000)
P = 55
Optimal price is $55, quantity is 50,000.
The difference between competitive outcome and the socially optimal outcome occurs because the private market is not capturing all of the costs.
c.To determine social loss, sketch the free market outcome.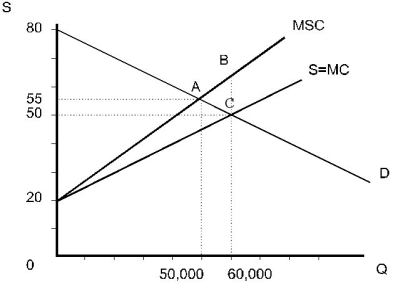 The free market outcome (point C) must be compared to the socially optimal outcome at point a.ABC is the loss to society. It represents the difference between MSC and demand for the units of output between 50,000 (optimal output) and 60,000 (competitive output).
The free market outcome (point C) must be compared to the socially optimal outcome at point a.ABC is the loss to society. It represents the difference between MSC and demand for the units of output between 50,000 (optimal output) and 60,000 (competitive output).
P = 80 - 0.0005QD
P = 20 + 0.0005QS
Equate demand and supply
80 - 0.0005Q = 20 + 0.0005Q
60 = 0.001Q
Q = 60,000
P = 20 + 0.0005(60,000)
P = 20 + 30
P = 50
b.Socially optimal level is where demand intersects MSC
MSC = MC + MEC
MC is equal to supply
MSC = (20 + 0.0005Q) + 0.0002Q
MSC = 20 + 0.0007Q
Equate demand to MSC
80 - 0.0005Q = 20 + 0.0007Q
60 = 0.0012Q
Q = 50,000
P = 20 + 0.0005(50,000)
P = 55
Optimal price is $55, quantity is 50,000.
The difference between competitive outcome and the socially optimal outcome occurs because the private market is not capturing all of the costs.
c.To determine social loss, sketch the free market outcome.
 The free market outcome (point C) must be compared to the socially optimal outcome at point a.ABC is the loss to society. It represents the difference between MSC and demand for the units of output between 50,000 (optimal output) and 60,000 (competitive output).
The free market outcome (point C) must be compared to the socially optimal outcome at point a.ABC is the loss to society. It represents the difference between MSC and demand for the units of output between 50,000 (optimal output) and 60,000 (competitive output).
Learning Objectives
- Recognize the influence of externalities on the effectiveness of markets and the optimal societal production and consumption rates.
- Recognize the principles of marginal private cost, marginal external cost, and marginal social cost.
- Compute the optimal level of production taking into account external costs.