Asked by Raabiah Azeez on May 09, 2024

Verified
Laura's internet services has the following short-run cost curve: 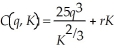 where q is Laura's output level, K is the number of servers she leases and r is the lease rate of servers. Laura's short-run marginal cost function is:
where q is Laura's output level, K is the number of servers she leases and r is the lease rate of servers. Laura's short-run marginal cost function is: 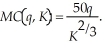 Currently, Laura leases 8 servers, the lease rate of servers is $15, and Laura can sell all the output she produces for $500. Find Laura's short-run profit maximizing level of output. Calculate Laura's profits. If the lease rate of internet servers rise to $20, how does Laura's optimal output and profits change?
Currently, Laura leases 8 servers, the lease rate of servers is $15, and Laura can sell all the output she produces for $500. Find Laura's short-run profit maximizing level of output. Calculate Laura's profits. If the lease rate of internet servers rise to $20, how does Laura's optimal output and profits change?
Short-Run Cost Curve
A graph showing the relationship between the cost of producing goods and the output level in the short term, when at least one input is fixed.
Lease Rate
The cost of renting a property, equipment, or other assets, typically expressed as a monetary payment per time period.
- Determine the level of output that maximizes profits for companies across different competitive landscapes and ascertain whether economic profits or losses are present.
- Evaluate the effects of technological innovation and input prices on a firm’s cost curves and optimal output.

Verified Answer
FM
Felicia MassonMay 11, 2024
Final Answer :
The profit maximizing output level is where the market price equals marginal cost (providing the price exceeds the average variable cost). To determine the optimal output level, we need to first equate marginal cost to the market price. That is, MC 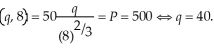 The average variable cost at this output level is:
The average variable cost at this output level is: 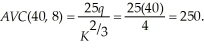 Since
Since 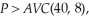 Laura will maximize profits at 4 units. Laura's profits are:
Laura will maximize profits at 4 units. Laura's profits are: 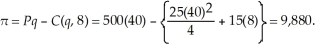 If the lease rate of servers rise to $20, Laura's short-run output level doesn't change as average variable cost and marginal cost are unaffected by the lease rate. Laura's profits will be affected. New profits are:
If the lease rate of servers rise to $20, Laura's short-run output level doesn't change as average variable cost and marginal cost are unaffected by the lease rate. Laura's profits will be affected. New profits are: 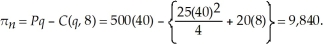 Thus, the $5 increase in the rental rate reduced Laura's short-run profits by $40.
Thus, the $5 increase in the rental rate reduced Laura's short-run profits by $40.
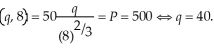 The average variable cost at this output level is:
The average variable cost at this output level is: 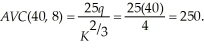 Since
Since 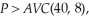 Laura will maximize profits at 4 units. Laura's profits are:
Laura will maximize profits at 4 units. Laura's profits are: 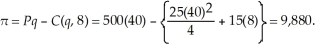 If the lease rate of servers rise to $20, Laura's short-run output level doesn't change as average variable cost and marginal cost are unaffected by the lease rate. Laura's profits will be affected. New profits are:
If the lease rate of servers rise to $20, Laura's short-run output level doesn't change as average variable cost and marginal cost are unaffected by the lease rate. Laura's profits will be affected. New profits are: 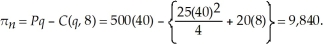 Thus, the $5 increase in the rental rate reduced Laura's short-run profits by $40.
Thus, the $5 increase in the rental rate reduced Laura's short-run profits by $40.
Learning Objectives
- Determine the level of output that maximizes profits for companies across different competitive landscapes and ascertain whether economic profits or losses are present.
- Evaluate the effects of technological innovation and input prices on a firm’s cost curves and optimal output.