Asked by Lanie Barnhill on Jun 08, 2024

Verified
Independent random samples of n1 = 150 and n2 = 150 sales phone calls for an insurance policy were randomly selected from binomial populations 1 and 2, respectively. Sample 1 had 80 successful sales, and sample 2 had 88 successful sales. Suppose you have no preconceived theory concerning which parameter, p1 or p2, is the larger and you wish to detect only a difference between the two parameters if one exists.
Calculate the standard error of the difference in the two sample proportions, 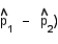 . Make sure to use the pooled estimate for the common value of p.
. Make sure to use the pooled estimate for the common value of p.
______________
Calculate the test statistic that you would use for the test above. Based on your knowledge of the standard normal distribution, is this a likely or unlikely observation, assuming that H0 is true and the two population proportions are the same?
Test statistic = ______________
Find the p-value for the test. Test for a significant difference in the population means at the 1% significance level.
p-value = ______________
Find the rejection region when 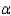 = 0.01. Do the data provide sufficient evidence to indicate a difference in the population proportions?
= 0.01. Do the data provide sufficient evidence to indicate a difference in the population proportions?
Critical Value(s) = ______________
Conclusion: ______________
Interpretation: __________________________________________
Independent Random Samples
Samples selected from a population in such a way that each member has an equal chance of being chosen, with no dependence between the selections.
Standard Error
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic, commonly used to estimate the accuracy of sample mean as a predictor of the population mean.
Pooled Estimate
Combining estimates from different populations to obtain a single estimate that is more accurate and has a higher power due to a larger sample size.
- Understand the process of constructing confidence intervals for the difference between two population proportions.
- Understand the analysis of test statistics and p-values within hypothesis testing concerning population proportions.
- Calculate and interpret the pooled estimate of proportion in hypothesis testing.

Verified Answer
CF
Courtney FraserJun 11, 2024
Final Answer :
0.0573; -0.94; 0.3472; 2.575, -2.575; Do not reject H0; There is NO evidence of a difference in the two population proportions

Learning Objectives
- Understand the process of constructing confidence intervals for the difference between two population proportions.
- Understand the analysis of test statistics and p-values within hypothesis testing concerning population proportions.
- Calculate and interpret the pooled estimate of proportion in hypothesis testing.