Asked by Alexia Montcerisier on May 16, 2024

Verified
In testing 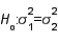 vs.
vs. 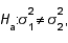 the null hypothesis will be rejected if the ratio
the null hypothesis will be rejected if the ratio 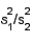 is substantially longer than 1.0.
is substantially longer than 1.0.
Null Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis that suggests there is no significant difference between specified populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error.
Ratio
A quantitative relationship between two numbers showing the number of times one value contains or is contained within the other.
- Understand the concept and application of F-distribution in hypothesis testing.
- Calculate the F-test statistic for comparing two sample variances.

Verified Answer
JJ
Joey Juvens PierreMay 22, 2024
Final Answer :
True
Explanation :
This statement is true. In hypothesis testing, if the ratio of the test statistic in the alternative hypothesis to the test statistic in the null hypothesis is substantially larger than 1.0, it suggests the alternative hypothesis is more likely to be true and the null hypothesis is rejected. Therefore, if the ratio 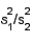 is substantially longer than 1.0, the null hypothesis would be rejected.
is substantially longer than 1.0, the null hypothesis would be rejected.
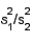 is substantially longer than 1.0, the null hypothesis would be rejected.
is substantially longer than 1.0, the null hypothesis would be rejected.
Learning Objectives
- Understand the concept and application of F-distribution in hypothesis testing.
- Calculate the F-test statistic for comparing two sample variances.