Asked by Daniela Lopez on Jul 11, 2024

Verified
In general, the binomial probability P(X 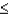 x) is approximated by the area under the normal curve to the left of x + - .5.
x) is approximated by the area under the normal curve to the left of x + - .5.
Normal Curve
A symmetric bell-shaped curve that represents the distribution of many types of data; most values remain near the mean and the frequencies decrease further from the mean.
Binomial Probability
The probability of obtaining a fixed number of successes in a set number of trials in an experiment with two possible outcomes.
Continuity Correction
A correction used in approximating a discrete distribution with a continuous one, especially in hypothesis testing with binomial distributions.
- Acquire knowledge on the concept of binomial probability and how it is approximated by the normal distribution.
- Identify the appropriate instances for implementing continuity correction within normal approximation.

Verified Answer

Learning Objectives
- Acquire knowledge on the concept of binomial probability and how it is approximated by the normal distribution.
- Identify the appropriate instances for implementing continuity correction within normal approximation.
Related questions
In General, the Binomial Probability P(X X) Is Approximated ...
In 1996, the Average Combined SAT Score (Math + Verbal) ...
In General,the Binomial Probability P(X ≤ X)is Approximated by the ...
A Sample of Size 200 Is Taken at Random from ...
Under Certain Conditions Where N Is Large Enough,you Can Approximate ...