Asked by Natasha Finkelstein on May 05, 2024

Verified
In a study to investigate the effect of diet on reducing cholesterol levels,a random sample of five subjects known to have high cholesterol had their cholesterol measured at the beginning of the study and after 6 months on a special diet.The data are given in the table below. 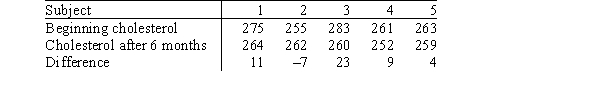 The data are to be analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed rank test.What is the standardized value z of W+?
The data are to be analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed rank test.What is the standardized value z of W+?
A) 0.40
B) 0.95
C) 1.48
D) 3.51
Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test
A non-parametric method for comparing two related samples, matched pairs, or repeated measurements on the same sample to evaluate if their population mean ranks are different.
Null Hypothesis
The presumption in statistical testing that there is no difference or effect, and any observed difference is due to sampling or experimental error.
Cholesterol Levels
A measurement of different types of cholesterol within the blood, important for assessing heart health.
- Gain insight into the deployment and analysis of the Wilcoxon signed rank test when working with paired data.

Verified Answer
YA
Yasmin AvilaMay 10, 2024
Final Answer :
C
Explanation :
The Wilcoxon signed rank test involves ranking the absolute differences between the paired observations and then summing up the ranks of the positive and negative differences separately. The test statistic is the smaller of these sums (W) and is compared to a critical value from the Wilcoxon signed rank distribution. In this case, W = 13.5. We can calculate the variance of the test statistic using the formula var(W) = [(n(n+1)(2n+1))/6 - sum(di^3 - di)/48], where n is the sample size and di is the ith absolute difference. In this case, n = 5 and the absolute differences are 85, 47, 48, 3, and 38. Plugging these values into the formula, we get var(W) = 10.5. The standardized value z can then be calculated as z = (W - )/sqrt(var(W)), where is the expected value of W under the null hypothesis of no difference in cholesterol levels. Since we expect half of the absolute differences to be positive and half to be negative by chance, = n(n+1)/4 = 7.5. Plugging in the numbers, we get z = (13.5 - 7.5)/sqrt(10.5) = 1.48. Therefore, the correct choice is C.

Learning Objectives
- Gain insight into the deployment and analysis of the Wilcoxon signed rank test when working with paired data.