Asked by Kelsee Katsanes on May 31, 2024

Verified
In a multiple regression model involving 50 observations, the following estimated regression equation was obtained: 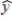 = 20 + 5x1 - 4x2 + 8x3 + 8x4
= 20 + 5x1 - 4x2 + 8x3 + 8x4
For this model, SSR = 700 and SSE = 100.At the 5% level,
A) there is no evidence that the model is significant.
B) it can be concluded that the model is significant.
C) the conclusion is that the slope of x1 is significant.
D) there is evidence that the slope of x2 is significant.
Estimated Regression Equation
An equation derived from regression analysis used to predict the dependent variable based on one or more independent variables.
SSR
Sum of Squares due to Regression, a measure used in statistical analysis to determine the explanatory power of a regression model.
SSE
Sum of Squared Errors, a measure of the discrepancy between the data and an estimation model.
- Discriminate among the diverse tests (t-test, F-test, chi-square test) utilized in the assessment of regression models.

Verified Answer

Learning Objectives
- Discriminate among the diverse tests (t-test, F-test, chi-square test) utilized in the assessment of regression models.
Related questions
The Following Estimated Regression Equation Was Developed Relating Yearly Income ...
In a Regression Analysis Involving 21 Observations and 4 Independent ...
{Real Estate Builder Narrative} at the 0 ...
{Real Estate Builder Narrative} What Is the Value of the ...
{Student's Final Grade Narrative} Does This Data Provide Enough Evidence ...