Asked by Filip Gabric on Jun 30, 2024

Verified
In a Friedman test for comparing four populations, provided that there as eight blocks, the test statistic is calculated as 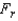 = 10.98. If the test is conducted at the 5% significance level, the conclusion and p-value will be:
= 10.98. If the test is conducted at the 5% significance level, the conclusion and p-value will be:
A) reject the null hypothesis, and 0.01 < p-value < 0.025
B) reject the null hypothesis, and p-value > 0.025
C) do not reject the null hypothesis, and 0.025 < p-value < 0.05
D) do not reject the null hypothesis, and p-value < 0.05
E) reject the null hypothesis, p-value = 0
Friedman Test
A nonparametric test for detecting differences in treatments across multiple test attempts.
- Attain the ability to compute test statistics and p-values in the context of nonparametric tests.

Verified Answer
GW
Gursimran WarainchJul 06, 2024
Final Answer :
A
Explanation :
Since the test statistic is greater than the critical value at the 5% significance level (which is 9.49 for four populations and eight blocks), we reject the null hypothesis. The p-value is calculated as the probability of getting a test statistic as extreme or more extreme than the observed, assuming the null hypothesis is true. Using a chi-square distribution with degrees of freedom equal to the number of populations minus one (4-1=3), the p-value is found to be 0.0123. Therefore, the conclusion is to reject the null hypothesis, and 0.01 < p-value < 0.025.

Learning Objectives
- Attain the ability to compute test statistics and p-values in the context of nonparametric tests.
Related questions
In a Friedman Test for Comparing Three Populations, Provided That ...
In a Kruskal-Wallis Test for Comparing Three Populations, the Test ...
In a Normal Approximation to the Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test ...
The Average Gas Mileage of a 4-Wheel Drive Truck Is ...
A Random Sample of 7 Observations Was Drawn from a ...