Asked by Jayson Sta Cruz on Jun 26, 2024

Verified
If we reject the null hypothesis 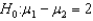 at the 0.01 level of significance, then we must also reject it at the 0.05 level.
at the 0.01 level of significance, then we must also reject it at the 0.05 level.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement used in statistical testing that proposes there is no significant difference or effect, serving as the default assumption to be tested against.
Level of Significance
The threshold below which a p-value is considered statistically significant, typically set at 0.05 or 5%, indicating the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true.
- Attain knowledge of and apply p-values in hypothesis testing to make decisions based on understanding.
- Assess the interpretations and implications of results derived from hypothesis testing, paying particular attention to Type I and Type II errors.

Verified Answer

Learning Objectives
- Attain knowledge of and apply p-values in hypothesis testing to make decisions based on understanding.
- Assess the interpretations and implications of results derived from hypothesis testing, paying particular attention to Type I and Type II errors.
Related questions
A University Investigation Was Conducted to Determine Whether Women and ...
In a One-Tailed Test, the P-Value Is Found to Be ...
When the Necessary Conditions Are Met, a Two-Tail Test Is ...
You Will Make the Decision to ______ When the Probability ...
{Sinus Drug Narrative} Is There Enough Evidence at the 5 ...