Asked by Jessica Shatteen on May 29, 2024

Verified
Given N = 1,000, n = 30, and 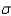 = 6, the standard error of the sample mean, SE
= 6, the standard error of the sample mean, SE 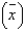 , equals:
, equals:
A) .009
B) .5
C) 5.5
D) 1.095
E) 33.33
Standard Error
A measure of the statistical accuracy of an estimate, equal to the standard deviation of the theoretical distribution of a large population of such estimates.
N
A symbol often used to represent a sample size or the number of observations or units in a dataset.
- Determine the average and variability measure for distributions derived from sampling.

Verified Answer
IH
Iffah HannaniJun 04, 2024
Final Answer :
D
Explanation :
The formula for the standard error of the sample mean is SE = (standard deviation of the population) / sqrt(sample size). We are not given the standard deviation of the population, so we will have to estimate it using the sample standard deviation. Assuming the sample is a representative sample of the population, we can use the sample standard deviation as an estimate of the population standard deviation.
Using the formula, we get:
SE = (sample standard deviation) / sqrt(sample size)
SE =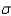 / sqrt(30)
/ sqrt(30)
SE = 1.095
Therefore, the answer is D) 1.095.
Using the formula, we get:
SE = (sample standard deviation) / sqrt(sample size)
SE =
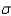 / sqrt(30)
/ sqrt(30)SE = 1.095
Therefore, the answer is D) 1.095.

Learning Objectives
- Determine the average and variability measure for distributions derived from sampling.