Asked by Johnny Davis on Apr 27, 2024

Verified
"Cramming" is a technique often used by students to prepare for exams,in which they study for extended hours only a few days before the exams.Often students drink caffeinated beverages to help them stay awake while cramming for exams.Five students were randomly selected and asked to drink highly caffeinated beverages before their first midterm exam and then drink only water before their second midterm exam in the same subject.The difference of the scores (midterm 2 - midterm 1) is shown below for the five students. 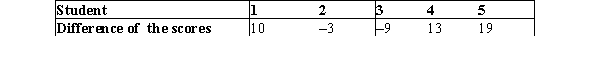 Using the continuity correction,what is the probability that needs to be calculated in order to obtain the P-value used to test the null hypothesis of no difference using the Wilcoxon signed rank test statistic?
Using the continuity correction,what is the probability that needs to be calculated in order to obtain the P-value used to test the null hypothesis of no difference using the Wilcoxon signed rank test statistic?
A) P(W+ 12)
B) P(W+ 11.5)
C) P(W+ 12.5)
D) None of the above
Continuity Correction
An adjustment made to discrete data in order to apply a continuous probability distribution approximation more accurately.
Null Hypothesis
A statement or hypothesis that proposes there is no statistical significance in a set of given observations, suggesting any observed difference is due to sampling or experimental error.
- Understand the computation and analysis of P-values within the context of hypothesis evaluation.

Verified Answer
CT
Cyndi TochimaniMay 01, 2024
Final Answer :
B
Explanation :
The Wilcoxon signed rank test statistic is based on the sum of the ranks of the differences between paired observations. In this case, the differences are the midterm scores (midterm 2 - midterm 1). We want to test the null hypothesis of no difference, which means the median of the differences is zero. The P-value is the probability of getting a test statistic as extreme or more extreme than the observed one under the null hypothesis. The continuity correction adjusts the test statistics by subtracting 0.5 from the rank of each difference when it equals zero. The formula for the test statistic is:
WS = min(U1, U2) + 0.5 * (U1+U2)(P0-P1)
where U1 and U2 are the sums of the ranks of the positive and negative differences, P0 is the number of pairs with zero difference, and P1 is the number of pairs with positive difference.
To calculate the P-value, we need to compare the observed test statistic to the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis. We can use the normal approximation to the distribution of the test statistic, which is valid for large sample sizes. The formula for the standard error of the test statistic is:
SE = sqrt((P0*P1/12)*(n*(n+1)-sumTies))
where n is the sample size and sumTies is the sum of the ties in the ranks of the differences.
Using the observed data, we have U1 = 11, U2 = 7, P0 = 1, and P1 = 3. The sum of the ties is 2.5. Therefore, the test statistic is:
WS = min(11, 7) + 0.5*(11+7)(1-3/4) = 11.5
The standard error is:
SE = sqrt((1*3/12)*(5*(5+1)-2.5)) = 2.419
The z-score is:
z = (11.5-0)/2.419 = 4.74
The P-value is:
P = 2*P(Z > 4.74) = 2*0.000004 = 0.000008
Therefore, the answer is B: P(W+ ≥ 11.5).
WS = min(U1, U2) + 0.5 * (U1+U2)(P0-P1)
where U1 and U2 are the sums of the ranks of the positive and negative differences, P0 is the number of pairs with zero difference, and P1 is the number of pairs with positive difference.
To calculate the P-value, we need to compare the observed test statistic to the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis. We can use the normal approximation to the distribution of the test statistic, which is valid for large sample sizes. The formula for the standard error of the test statistic is:
SE = sqrt((P0*P1/12)*(n*(n+1)-sumTies))
where n is the sample size and sumTies is the sum of the ties in the ranks of the differences.
Using the observed data, we have U1 = 11, U2 = 7, P0 = 1, and P1 = 3. The sum of the ties is 2.5. Therefore, the test statistic is:
WS = min(11, 7) + 0.5*(11+7)(1-3/4) = 11.5
The standard error is:
SE = sqrt((1*3/12)*(5*(5+1)-2.5)) = 2.419
The z-score is:
z = (11.5-0)/2.419 = 4.74
The P-value is:
P = 2*P(Z > 4.74) = 2*0.000004 = 0.000008
Therefore, the answer is B: P(W+ ≥ 11.5).

Learning Objectives
- Understand the computation and analysis of P-values within the context of hypothesis evaluation.
Related questions
According to the 2004 Canadian Community Health Survey,23 \(\mathrm { H ...
The Management of a Water Park Has Concerns About the ...
A University Wants to Increase Its Retention Rate of 4 \(\mathrm ...
According to the 2004 Canadian Community Health Survey,23 ...
In Order to Determine Whether or Not There Is a ...