Asked by Jayla Barwari on May 21, 2024

Verified
Consider the following hypothesis test:
H0: p 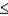 .8
.8
Ha: p > .8
A sample of 400 provided a sample proportion of .853.
a.
Determine the standard error of the proportion.
b.
Compute the value of the test statistic.
c.
Determine the p-value; and at a 5% level, test the above hypotheses.
Sample Proportion
The ratio of members in a statistical sample that have a particular attribute to the total number of members in the sample.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement used in statistics that proposes there is no significant difference or effect, serving as the starting point for hypothesis testing.
Alternative Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis that proposes a difference or effect, contrasting the null hypothesis.
- Ascertain the standard error of the mean as well as the standard error of proportion.
- Compute the test statistic for different kinds of hypothesis testing.
- Compute and elucidate p-values within the framework of hypothesis examination.

Verified Answer
VC

Learning Objectives
- Ascertain the standard error of the mean as well as the standard error of proportion.
- Compute the test statistic for different kinds of hypothesis testing.
- Compute and elucidate p-values within the framework of hypothesis examination.