Asked by Tristan Zuidema on May 26, 2024

Verified
A statistics professor posted the following grade distribution guidelines for his elementary statistics class: 8% A, 35% B, 40% C, 12% D, and 5% F. A sample of 100 elementary statistics grades at the end of last semester showed 12 As, 30 Bs, 35 Cs, 15 Ds, and 8 Fs. Test at the 5% significance level to determine whether the actual grades deviate significantly from the posted grade distribution guidelines. 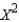 = ______________
= ______________
Critical Value = ______________
Conclusion: ______________
The actual grades ______________ from the posted grade distribution guidelines.
Grade Distribution
The spreading out of marks achieved by students in a course, often visualized using graphs or tables to understand the performance and grading trends.
Significance Level
The threshold below which the p-value of a statistical test must fall for the null hypothesis to be rejected, indicating statistical significance.
Sample
A subset of a population selected for measurement, observation, or questioning, to provide statistical information about the population.
- Learn to apply and comprehend hypothesis testing strategies for proportional analyses.
- Compute critical values and assess test statistics across different tests.
- Inspect data to conclude if it upholds a proposed hypothesis or claim.

Verified Answer
JS

Learning Objectives
- Learn to apply and comprehend hypothesis testing strategies for proportional analyses.
- Compute critical values and assess test statistics across different tests.
- Inspect data to conclude if it upholds a proposed hypothesis or claim.